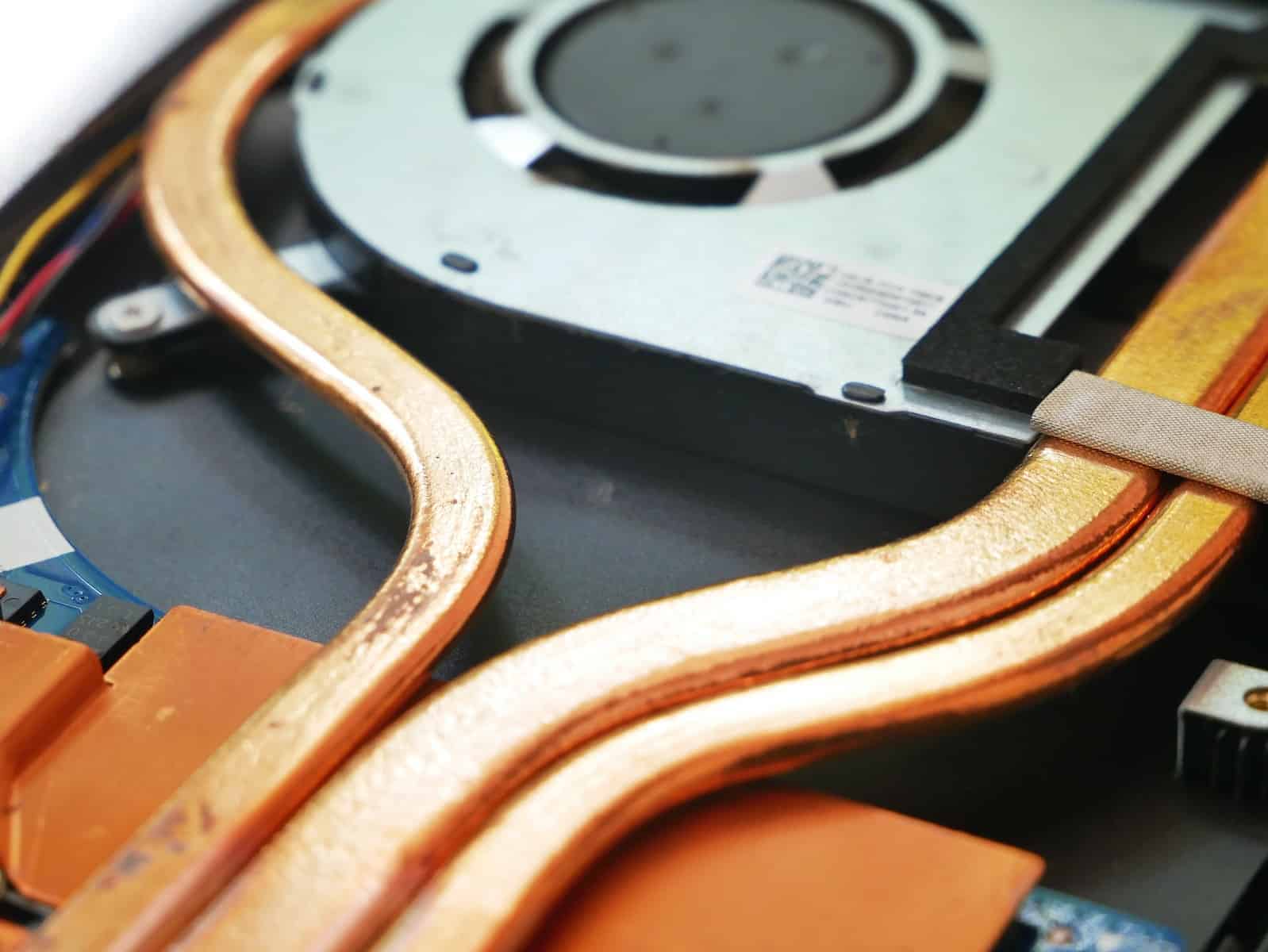
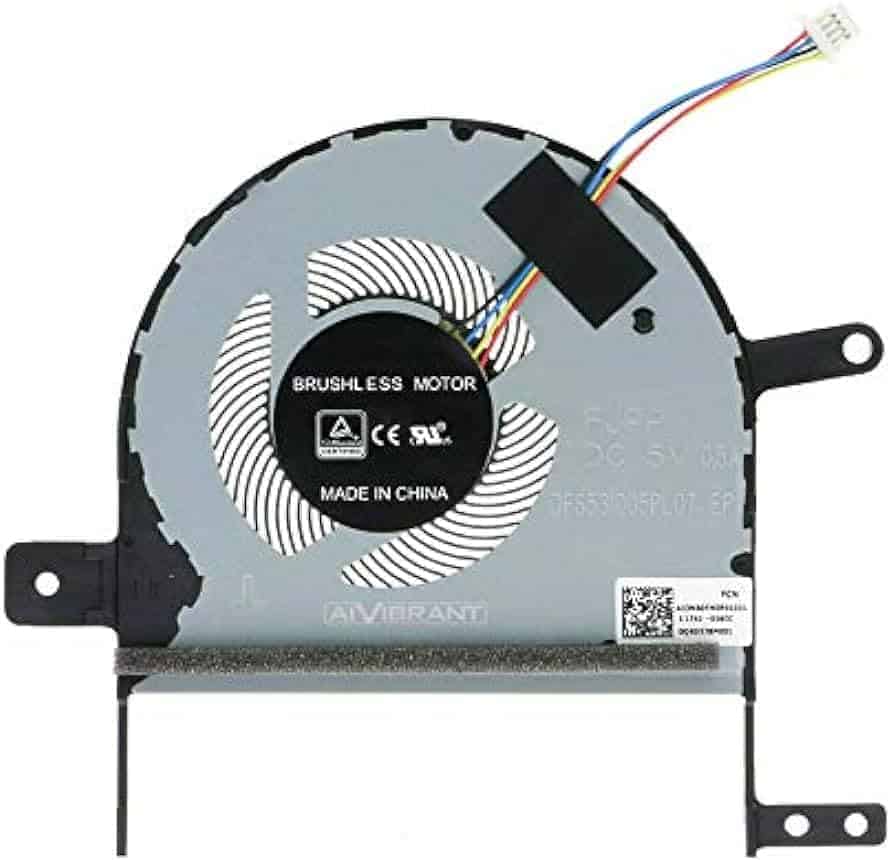
A laptop’s CPU cooler is a small fan and heatsink combo. It sits on top of the processor. The cooler draws heat away from the CPU and blows it out of the laptop case. This keeps the processor from getting too hot while it works.
Most laptop CPU coolers are thin. They have to fit in the tight space inside a laptop. The fan part is usually round or square. It spins to move air over the heatsink. The heatsink is made of metal fins that spread out the heat. Together, they work to keep the CPU cool.
Laptop CPU coolers are smaller than desktop ones. But they do the same job. They stop the processor from overheating. This helps the laptop run better and last longer.

Cooling Down Your Laptop’s Brain: CPU Cooler Components
Heat Sink: The Cooling Core
The heart of any laptop CPU cooler is the heat sink. It’s a chunky piece of metal, usually copper or aluminum, designed to absorb heat from the CPU. Its many fins increase the surface area, allowing for better heat dissipation.
Heat Pipes: The Heat Highways
Think of heat pipes as tiny highways for heat transfer. They contain a liquid that vaporizes when heated, carrying the heat away from the CPU. The vapor cools and condenses, returning to the CPU to pick up more heat. It’s a continuous cycle of heat transfer.
Thermal Paste: The Heat Conductor
Thermal paste is a thin layer of material applied between the CPU and the heat sink. It fills microscopic gaps and improves thermal conductivity, ensuring efficient heat transfer from the CPU to the heat sink.
Fan(s): The Air Movers
Fans are the unsung heroes of CPU cooling. They blow cool air over the heat sink, carrying away the absorbed heat. The number and size of fans can vary depending on the laptop’s design and cooling requirements.
Additional Cooling Elements
Some laptops have additional cooling features like vapor chambers or liquid cooling systems. These offer even greater cooling efficiency but are typically found in high-performance laptops.
Types of CPU Coolers
Laptop CPU coolers come in various designs, but they all share the same basic components.
| Cooler Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Passive Cooler | Relies solely on the heat sink and thermal paste for cooling. No fan is involved. |
| Active Cooler | Uses a fan in addition to the heat sink and thermal paste to actively move heat away from the CPU. |
| Vapor Chamber Cooler | Employs a vapor chamber, a flat heat pipe filled with a small amount of liquid for more efficient cooling. |
| Liquid Cooling System | Circulates a liquid coolant through a closed loop to cool the CPU. Often found in high-performance gaming laptops. |
Key Takeaways
- Laptop CPU coolers use a fan and heatsink to remove heat
- They are thin to fit inside the small laptop case
- Good cooling helps laptops run faster and live longer
Understanding CPU Cooling Technologies
CPU cooling keeps laptops from overheating. It uses different methods to remove heat from the processor.
Air Cooling Mechanisms
Air cooling is common in laptops. It uses fans and heatsinks to move hot air away from the CPU. The heatsink is a metal piece with fins that sits on top of the CPU. It spreads out heat from the processor.
Thermal paste helps transfer heat between the CPU and heatsink. Fans blow cool air over the heatsink fins. This cools the metal and takes away heat. Some laptops have heat pipes too. These are thin tubes that move heat from the CPU to other parts of the laptop.
Air coolers are simple and cheap. But they can be noisy when working hard.
Liquid Cooling Systems
Liquid cooling is less common in laptops. It uses special fluids to take away heat. A pump moves coolant through tubes near the CPU. The liquid absorbs heat and carries it to a radiator.
The radiator has many thin fins. A fan blows air over these fins to cool the liquid. Then the cool liquid flows back to the CPU. This process keeps going to maintain low temperatures.
Liquid cooling is very good at keeping CPUs cool. It’s often quieter than air cooling. But it costs more and needs more upkeep. Some gaming laptops use this system for better cooling.
Selecting the Right CPU Cooler for Your System
Picking a CPU cooler involves weighing several key factors. The right choice depends on your specific needs and system setup.
Factors That Influence CPU Cooler Choice
CPU socket type is crucial when selecting a cooler. Different sockets need different mounting brackets. Check your motherboard’s socket before buying. TDP (Thermal Design Power) is also important. It shows how much heat your CPU makes. Choose a cooler that can handle your CPU’s TDP.
Your budget matters too. Air coolers are often cheaper than liquid ones. But liquid coolers can be better for high-end CPUs. Case size affects your options as well. Make sure the cooler fits in your PC case. Some big air coolers might not fit in small cases.
Noise level is another factor to think about. Some coolers are quieter than others. This is key if you want a silent PC.
Design and Build Considerations
Air coolers use metal fins and fans to move heat. They’re simple and reliable. Liquid coolers use water to take heat away from the CPU. They can be more effective for very hot CPUs.
The cooler’s build quality is vital. Good materials help it last longer. Copper and aluminum are common in good coolers. Fan quality affects both cooling and noise. Better fans cool more and make less noise.
Some coolers have RGB lights. These can make your PC look nice. But they don’t help with cooling. Low-profile coolers are good for small cases. But they might not cool as well as bigger ones.
Aftermarket coolers often work better than stock ones. They can help if you want to overclock your CPU. But they cost extra.
Frequently Asked Questions
Laptop CPU cooling systems come in various forms. Users often have questions about identifying and optimizing their laptop’s cooling setup.
What methods are used to cool CPUs in laptops?
Laptops use fans and heat pipes to cool CPUs. Fans blow hot air out of vents. Heat pipes move heat away from the processor. Some laptops have vapor chambers for better cooling. Thermal paste helps transfer heat from the CPU to the cooler.
How can a user determine the type of CPU cooler in their laptop?
Users can check their laptop’s manual or specs online. Opening the laptop case shows the cooler type. Software tools give info on fan speeds and temps. Looking at vents and listening for fan noise also helps identify the cooling system.
Are there different categories of CPU coolers available for laptops?
Laptops have two main cooler types: air and liquid. Air coolers use fans and heat sinks. Liquid coolers use special fluids to remove heat. Most laptops use air cooling. Some high-end gaming laptops have liquid cooling systems.
Do cooling pads effectively lower temperatures in laptops?
Cooling pads can help reduce laptop temps. They add extra fans below the laptop. This improves airflow and heat removal. The effect varies based on the pad’s quality and the laptop’s design. They work best for laptops with poor built-in cooling.
What are the best cooling solutions for gaming laptops?
Gaming laptops need strong cooling. Good options include:
- Laptops with multiple fans
- Models with large heat pipes
- Systems with vapor chamber cooling
- Undervolting the CPU
- Using a high-quality cooling pad
Regular cleaning of vents and fans also helps keep gaming laptops cool.
How does liquid cooling compare to traditional cooling methods in laptops?
Liquid cooling is more efficient than air cooling. It moves heat away from the CPU faster. This allows for better performance and quieter operation. But liquid cooling systems are rare in laptops. They’re complex and costly to make. Most laptops stick with air cooling for simplicity and reliability.