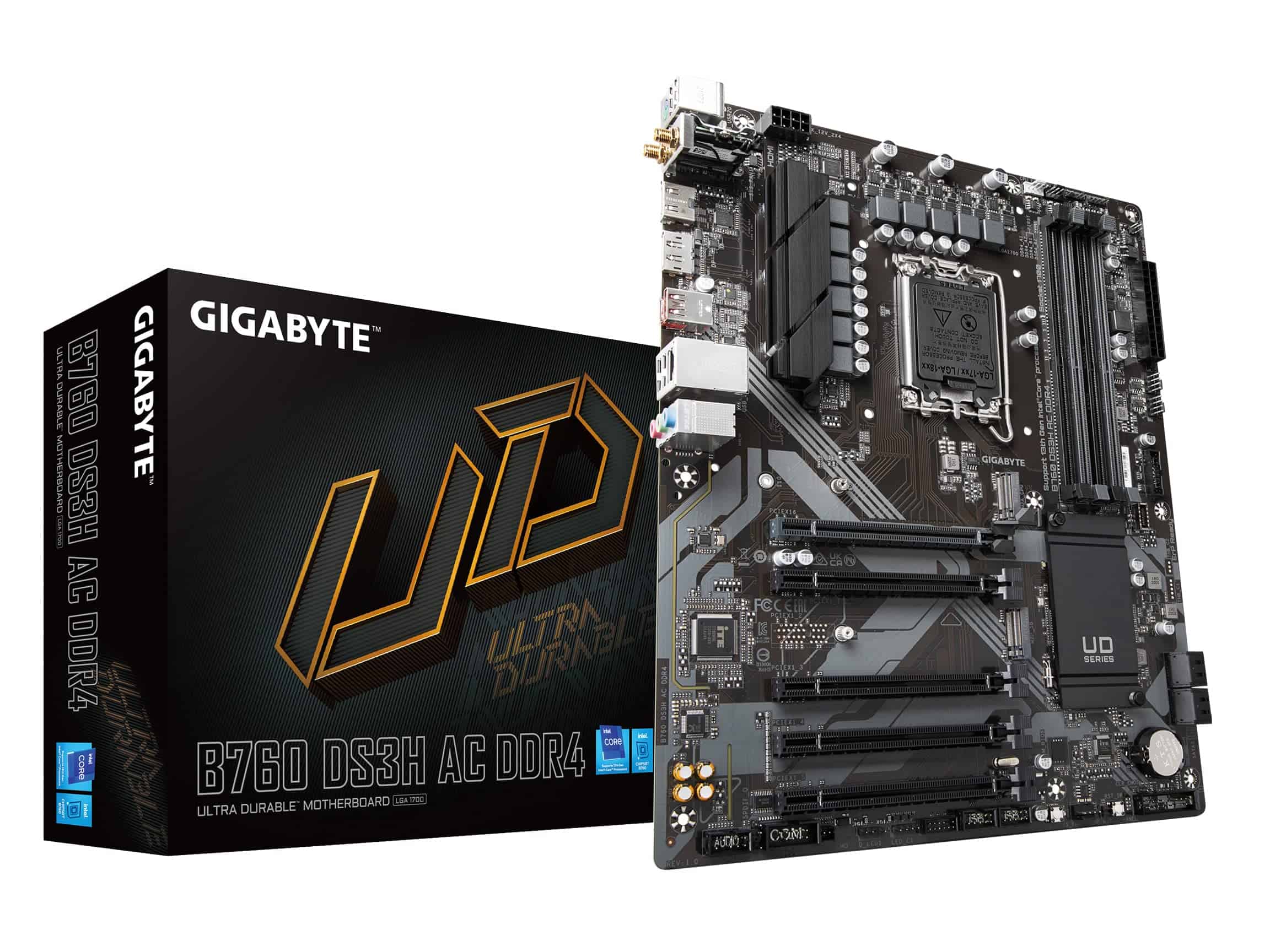
When building or upgrading a computer, the motherboard is a critical component that determines the PC’s capabilities. The motherboard acts as the main hub, ensuring all other parts, such as the CPU, RAM, and expansion cards, communicate effectively. Certain features on motherboards are essential for compatibility and performance. For example, PCIe slots on a motherboard are used for adding graphics cards, sound cards, and other expansion cards, with various slot sizes available depending on the card requirements.
Another vital specification is the compatibility with CPUs, which is often linked to the motherboard’s chipset and socket type. Matching the motherboard with a CPU that fits and is supported by the chipset ensures that the PC can operate at its intended performance level. RAM slots are also an area of consideration, determining how much and what type of RAM a user can install, which in turn affects the computer’s speed and multitasking capabilities.
Motherboard Specifications: Your PC’s Backbone
Motherboards are the unsung heroes of computers, connecting and powering all components. Understanding their specs is key to building or upgrading your PC.
What is a Motherboard?
Think of a motherboard as the central nervous system of your computer. It’s a large circuit board that houses the CPU, RAM, storage drives, and expansion cards. It also provides connections for peripherals like keyboards, mice, and monitors.
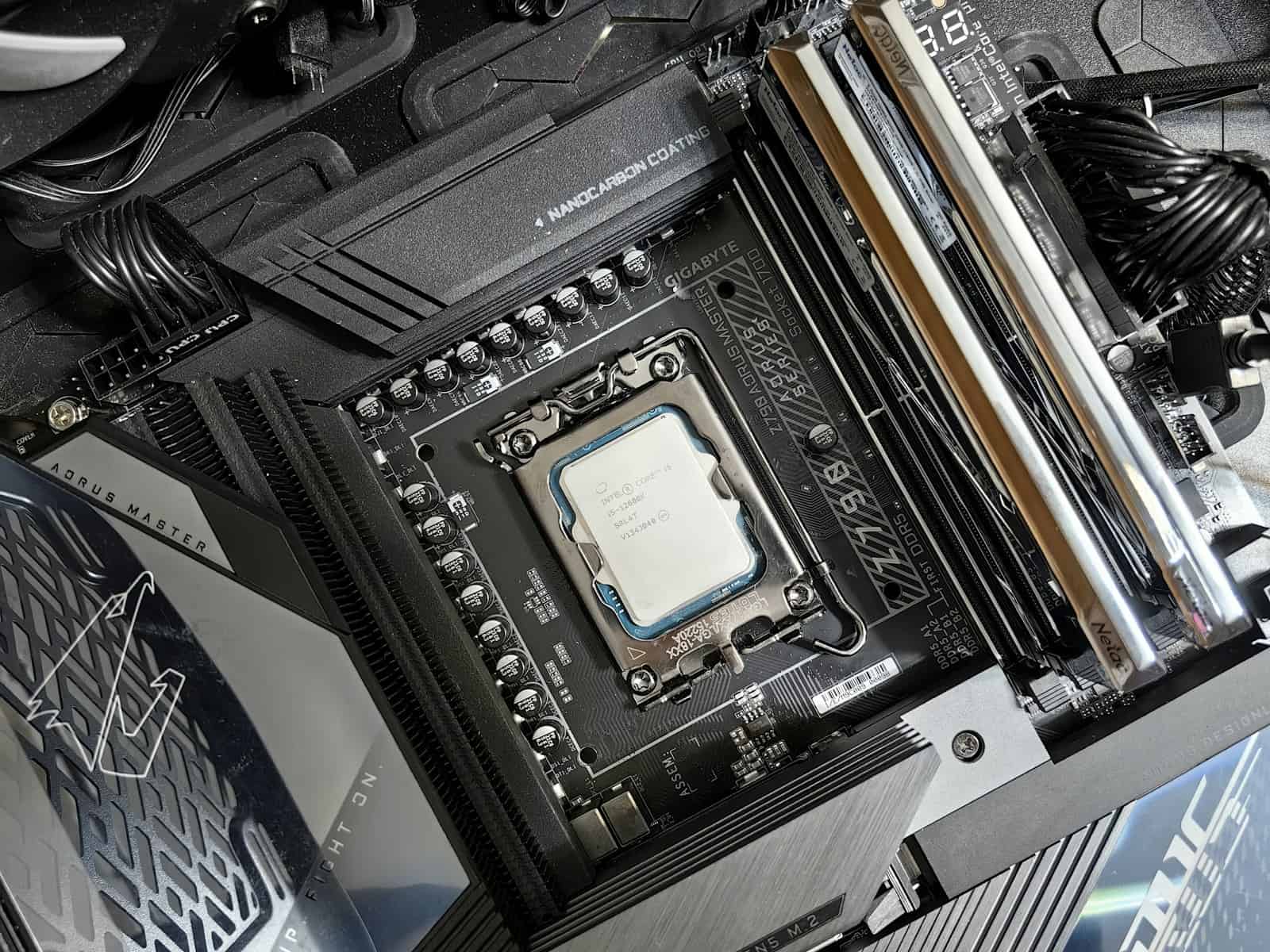

Key Motherboard Specifications
- Form Factor: This determines the motherboard’s size and layout. Common form factors include ATX, Micro ATX, and Mini ITX. Choose a form factor that fits your case and component needs.
- Socket: This is where the CPU goes. Make sure your CPU is compatible with the motherboard’s socket. Common sockets include LGA 1700 for Intel and AM5 for AMD.
- Chipset: This determines the motherboard’s features and compatibility. Chipsets vary between manufacturers and generations, so choose one that supports your desired features.
- RAM Slots: These hold the memory modules. Consider the number of slots, maximum capacity, and supported speed. DDR5 is the latest standard, but DDR4 is still widely used.
- Storage: Look for M.2 slots for NVMe SSDs (fastest storage) and SATA ports for traditional SSDs or HDDs. The number and types of ports determine your storage options.
- Expansion Slots: These accommodate graphics cards, sound cards, and other add-ons. PCIe is the most common type, with varying lengths and speeds.
- Rear I/O Panel: This provides ports for connecting external devices. Look for USB ports, audio jacks, Ethernet, and display outputs (HDMI, DisplayPort).
Table of Common Motherboard Features
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Form Factor | Size and layout of the motherboard | Determines case compatibility and component space. |
| Socket | Connection for the CPU | Ensures CPU compatibility. |
| Chipset | Determines features and compatibility | Affects overall performance and upgrade potential. |
| RAM Slots | Holds memory modules | Determines maximum memory capacity and speed. |
| Storage | M.2 and SATA ports for SSDs and HDDs | Affects storage capacity and speed. |
| Expansion Slots | Accommodates graphics cards and other add-ons | Determines expansion capabilities. |
| Rear I/O Panel | Provides ports for external devices | Affects connectivity options. |
Choosing the Right Motherboard
When choosing a motherboard, consider your budget, CPU, desired features, and future upgrade plans. Do your research, read reviews, and compare specifications to find the best fit for your needs.
Remember, the motherboard is the foundation of your computer. A well-chosen motherboard can significantly impact your PC’s performance, stability, and upgradeability.
Key Takeaways
- Motherboard compatibility with CPUs and RAM is critical for performance.
- PCIe slots on a motherboard are used to add various expansion cards.
- Matching all components to the motherboard specifications is essential for building an effective PC.
Understanding Motherboard Architecture
The motherboard is the central hub that determines a PC’s capabilities and potential for upgrades. This section explains the key components and features that define motherboard architecture.
Form Factors
Motherboard size is crucial for ensuring the motherboard fits in the selected PC case. Common form factors include:
- ATX: Measures 12″ x 9.6″ and is widely used due to its compatibility with multiple expansion slots.
- Micro-ATX: Slightly smaller at 9.6″ x 9.6″, it’s beneficial for compact builds.
- Mini-ITX: At 6.7″ x 6.7″, it’s designed for small form factor PCs.
- E-ATX: Larger than ATX, offering additional space for more features.
CPU Sockets and Chipsets
The CPU socket is specific to the processor brand:
- Intel‘s LGA: Land Grid Array varies by processor generation.
- AMD uses predominantly the AM4 socket for its CPUs.
Chipsets moderate the communication between the CPU and other parts of the system. They define the motherboard’s features, like USB ports or the number of SATA connections, and also affect CPU compatibility.
Memory and Expansion Slots
Motherboards include RAM slots for memory and PCIe slots for expansion cards:
- RAM slots determine how much and what type of RAM the motherboard can support.
- PCIe slots vary from PCI x1 to PCIe x16, with the latter mainly used for GPUs.
Storage Interfaces
Storage connectivity involves several types of connectors:
- SATA ports for HDDs and SSDs.
- M.2 slot supports NVMe SSDs for faster data transfer rates.
Rear Panel Connectors
These are the ports on the back of the PC:
- Various USB ports, including USB-C and Thunderbolt.
- Network connectivity through an Ethernet port.
- Display outputs like HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI, and VGA.
Internal Connectors and Headers
Connectors within the motherboard include:
- CPU power connector: Supplies power to CPU.
- Fan headers: Connect PC cooling fans.
- Front panel header: Connects power button and activity LEDs.
- Various USB headers like USB 2.0, USB 3.1 Gen1, and USB 3.1 Gen2.
Power Supply and Performance
Motherboards have an ATX power connector providing power to the board and onboard hardware. High-end motherboards contain a more robust VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) with multiple phases for stable power delivery and better overclocking performance.
Networking and Additional Features
Motherboards may have integrated Ethernet controllers and possibly Wi-Fi. Additional features can include onboard sound cards, thermal sensors, and additional peripherals support. Cooling systems might incorporate a VRM heatsink to manage high temperatures.