The power management setting “Put hard disks to sleep when possible” can be found in computer operating systems like macOS. It helps save energy by allowing the hard drive to enter a low power state when not in use. This feature is located in the Energy Saver section for desktops or the Battery section for laptops. Managing this setting is important for optimizing power usage. By configuring hard disk sleep options, users can extend battery life on portable devices or reduce power draw on desktop computers. While enabling this feature may cause a brief delay when accessing stored data after a period of inactivity, the benefits of conserving power often outweigh this inconvenience.
“Put Hard Disks to Sleep When Possible” is a setting on a Mac that allows the hard disks to enter a sleep state when it’s possible. To turn this setting on, you can do the following:
- Select the Apple menu
- Select System Settings
- Select Battery or Energy Saver in the sidebar
- Select Options or Enable Power Nap on the right
- Turn on Put hard disks to sleep when possible
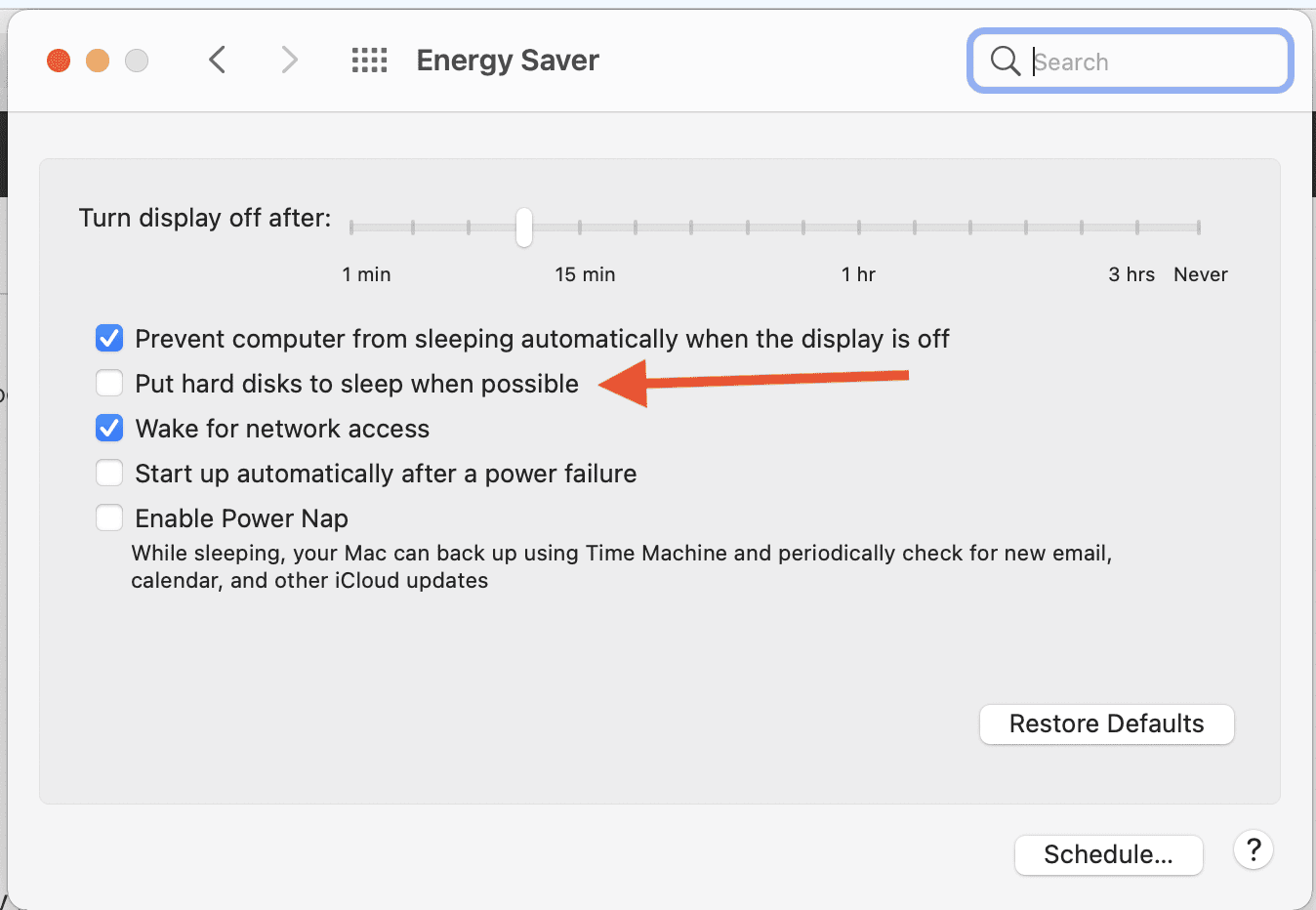
Some recommend changing this setting to prevent problems when allowing external storage devices to sleep. To do this, you can deselect “Put hard disks to sleep when possible” from the Energy Saver window.
Understanding Hard Drive Sleep for Improved Performance
“Put Hard Disks to Sleep When Possible” is a setting found in many operating systems. It offers the potential for some great benefits, but it’s important to understand how it works before you make changes.
What happens when you enable “Put Hard Disks to Sleep When Possible”
This setting allows your computer to stop your hard drive from spinning when it’s not being used for a certain period of time. Hard drives have moving parts, so putting them to sleep helps them in a few ways:
- Reduced Power Consumption: Your hard drive won’t use as much electricity, which can be helpful for laptops and other battery-powered devices.
- Lowered wear and tear: The less your hard drive spins, the longer it may last.
- Quieter Operation: Hard drives can sometimes get noisy, so putting them to sleep can cut down on noise.
Is there a downside?
The one trade-off of using this power-saving feature is a slightly longer wait time when you need to use your hard drive again. It has to physically “wake up” and spin back up to speed before you can access data. For most everyday uses, this delay is very minor.
Should you enable this setting?
Here’s a quick table to help you decide:
| Situation | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Laptop or device where battery life is important | Enable |
| Desktop computer where power usage is less of a concern | Optional |
| Device with an SSD (Solid State Drive) | Disable (SSDs don’t have moving parts so the setting won’t help) |
How to change the “Put Hard Disks to Sleep When Possible” setting
The exact steps will vary based on your operating system (Windows, macOS, etc.), but you’ll typically find this option within your computer’s power or energy settings.
Key Takeaways
- The hard disk sleep feature helps conserve energy by powering down the drive when not in active use.
- Managing this setting optimizes power usage and can prolong battery life on portable devices.
- Users can easily adjust this option in the system settings to balance performance with energy efficiency.
Understanding Power Management in MacOS
MacOS offers various settings to manage your device’s power effectively. These settings help extend the battery life for MacBooks and decrease energy consumption for desktop Macs.
Energy Saver Preferences
Energy Saver in MacOS lets users manage their computer’s energy use. Users can access these preferences in System Settings. They can adjust settings for different scenarios, like when using battery power or when plugged into an outlet.
Hard Disk Sleep Settings
The “Put hard disks to sleep when possible” setting helps save power. For Macs with traditional hard drives, this setting reduces energy use by stopping the drive when it’s not active. Mac models with solid-state drives (SSDs), like the MacBook Air with M1 chip, don’t have mechanical parts so this setting does not affect them.
Battery and Power Settings
MacBook Pro and MacBook Air users can tailor their power settings for battery or adapter use. Adjusting these settings helps optimize energy use and battery life. Desktop Macs like the Mac Mini also offer power management settings tailored for desktop use.
Configuring Hard Disk Sleep Options
Many laptop and desktop computers offer settings to help conserve energy by putting hard drives to sleep after a period of inactivity. Understanding how to adjust these settings can lead to improved energy efficiency and potentially prolong the life of your drives.
Steps to Set Sleep and Wake Settings
On macOS, you can configure your hard drive sleep options by following these steps:
- Open System Settings from the Apple menu.
- Scroll to and select Battery on laptops or Energy Saver on desktops.
- Choose when to turn off the display and if the computer should go to sleep after periods of inactivity.
- Below the Battery or Energy Saver options, find Put hard disks to sleep when possible and select your preferred setting.
For Windows 10 users, follow these instructions:
- Open the Control Panel and select Power Options.
- Click on Change plan settings next to your active power plan.
- Click Change advanced power settings.
- In the new window, expand the Hard disk and then the Turn off hard disk after setting to configure the inactivity duration.
Power Nap and Related Features
On a Mac, Power Nap allows your computer to perform tasks like checking for new emails or system updates while it’s asleep. To turn it on,
- Navigate to Energy Saver or Battery in the System Settings.
- There should be an option called Enable Power Nap; checking it will activate the feature while your Mac is plugged into a power source or, for laptops, while on battery power.
Make sure that Wake for network access is toggled on if you want your Mac to be accessible on the network even when it’s asleep.
Optimizing Hard Drive Energy Efficiency
To maximize the energy efficiency of your hard disks, consider these points:
- SSDs (solid-state drives) don’t have moving parts, so they use less power compared to HDDs (hard disk drives). If you have an SSD, it may not be necessary to put it to sleep as frequently.
- External hard drives can also be set to sleep and will generally spin down after the period of inactivity you’ve defined.
- In laptop settings, you may find options to Prevent automatic sleeping on battery when the display is off or Prevent automatic sleeping when the display is off. Adjust these carefully to balance between energy savings and accessibility needs.
By configuring the hard disk sleep settings appropriately, you can save energy and reduce wear on your drives without significant interruptions to your workflow.
Frequently Asked Questions
The ‘Put hard disks to sleep when possible’ is a power-saving option on Mac computers designed with the aim of conserving energy and reducing power consumption. The feature has implications for performance, system functionality, and hardware longevity. Below are common questions users might have about this setting.
How does the ‘Put hard disks to sleep when possible’ setting affect Macbook Pro performance?
When enabled, a Macbook Pro’s hard disk enters a low-power state during periods of inactivity. This might lead to a slight delay when the disk is accessed again, as the drive needs to spin up to resume normal operations.
Why is the ‘Put hard disks to sleep when possible’ option missing after updating to macOS Ventura?
Users might notice this option is no longer visible after an update. This could occur if the system uses an SSD, as solid-state drives do not require ‘sleep’ settings. Apple may remove the option for systems that don’t benefit from it.
How can the ‘Put hard disks to sleep when possible’ feature be disabled on macOS?
To disable this feature, users can access the ‘Energy Saver’ section in System Preferences on Mac desktops or ‘Battery’ settings on Mac laptops. Uncheck the ‘Put hard disks to sleep when possible’ option to keep the disks running continuously.
What is the impact of ‘Put hard disks to sleep when possible’ on SSDs in Mac computers?
Solid-state drives (SSDs) have no moving parts, so the ‘Put hard disks to sleep when possible’ setting has minimal effect on them. SSDs inherently consume less power and wake from sleep much faster than traditional spinning disks.
Does enabling ‘Put hard disks to sleep when possible’ improve the longevity of a Macbook’s hard drive?
The reduced mechanical operation from sleeping can potentially prolong a hard drive’s lifespan. Having the drive operate less may reduce wear over time, but this benefit should be weighed against any inconvenience from waiting for drives to spin up.
Can the ‘Put hard disks to sleep when possible’ setting cause any damage to HDDs during sleep mode?
This setting is unlikely to harm traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). Drives are designed to enter sleep mode safely, and this feature makes use of that design to reduce power draw without risking hardware damage.