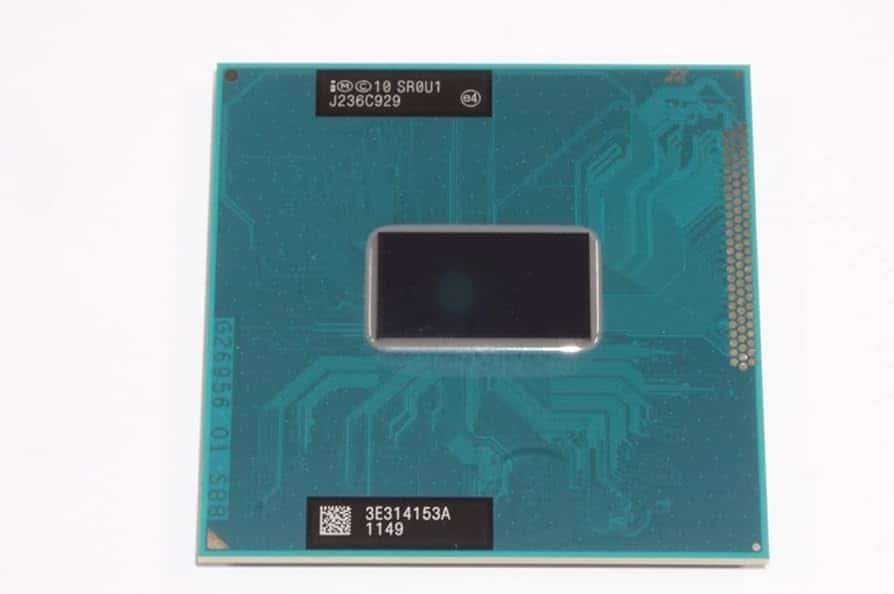
Intel processors often have letters after their model numbers, which provide important information about the CPU, and the letters “FMB” on Intel CPUs stand for “Flexible Motherboard.” This indicates that the processor can work with different types of motherboards.
The way a CPU is packaged is crucial for its performance and efficiency. FMB, or Flip-chip Multi-BGA, is an example of Intel’s innovative packaging techniques. By flipping the processor die and using a dense array of solder balls, FMB enables faster communication, lower power consumption, and more compact designs. This significantly contributes to the capabilities of modern computing devices. FMB CPUs offer more options for buyers as they can fit in systems with various chipsets and features, making them suitable for those who want to upgrade their computers or build new ones with existing parts.
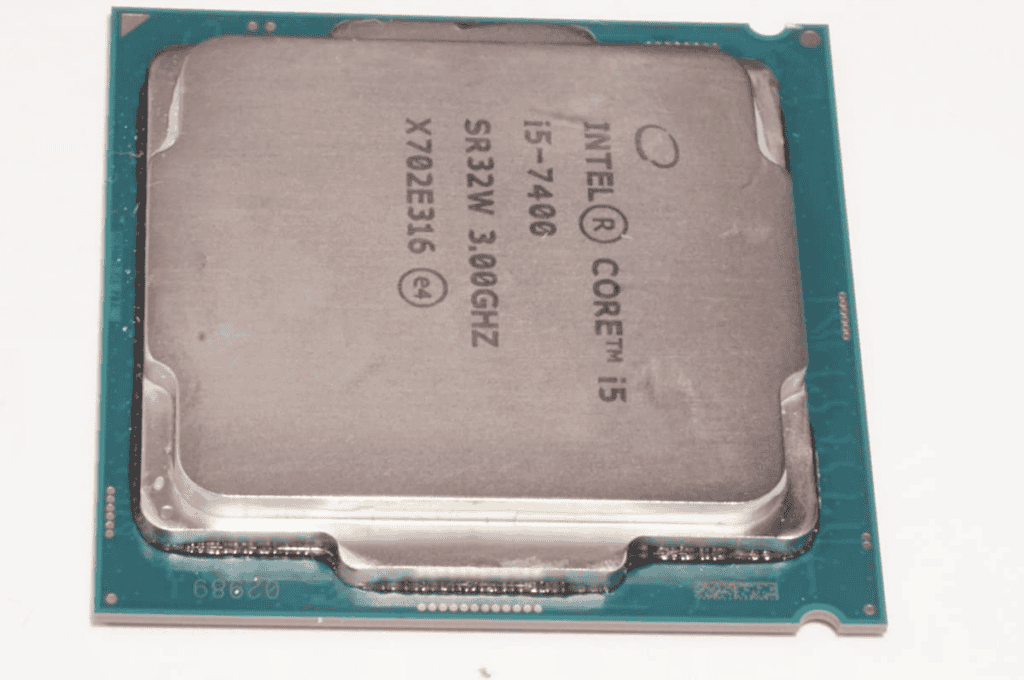

Intel uses many other letter codes, each providing information about the CPU’s capabilities. Understanding these codes helps shoppers choose the right processor for their needs.
Understanding Intel CPU Designations
Decoding FMB
FMB on an Intel CPU stands for Flip-chip Multi-BGA. This refers to a specific packaging technique used for the processor. Let’s break down what that means.
Flip-Chip
In flip-chip technology, the processor die (the small chip containing the CPU’s core) is flipped upside down. This allows the connections (electrical contacts) on the die to be directly connected to the substrate (the base of the package). This results in shorter electrical paths, which can improve performance and reduce power consumption.
Multi-BGA
BGA stands for Ball Grid Array. It’s a type of packaging that uses an array of tiny solder balls to connect the processor to the motherboard. “Multi” in this context likely signifies a higher density of these solder balls, providing more connection points for better signal integrity.
Why FMB Matters
FMB packaging is a key element in Intel’s processor design. It contributes to improved performance, reduced power consumption, and smaller form factors. These factors are essential for modern computing devices, especially laptops and mobile devices where space and battery life are critical.
Other Packaging Designations
Intel uses various packaging designations for its CPUs. Here are a few others you might encounter:
| Designation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| FCBGA | Flip-Chip Ball Grid Array |
| PGA | Pin Grid Array (older technology with pins instead of solder balls) |
| LGA | Land Grid Array (uses contact pads instead of pins) |
Keeping Up with Technology
As technology evolves, processor packaging techniques continue to advance. FMB is one example of how Intel innovates to improve performance and efficiency. By understanding these designations, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of modern CPUs.
Key Takeaways
- FMB means Flexible Motherboard for Intel CPUs
- These processors work with many types of motherboards
- Intel uses letter codes to show CPU features
Understanding Intel Processor Suffixes and FMB
Intel uses letters and numbers to name their CPUs. These codes tell us about the chip’s features and power.
Key to Intel Processor Suffixes
Intel adds letters to the end of CPU names. These letters give us clues about what the chip can do.
- K means the CPU can be overclocked
- F shows there’s no built-in graphics
- T points to a low-power chip
- H is for high-performance laptop CPUs
- U stands for ultra-low power in laptops
- Q means it has four cores
Some CPUs have more than one letter. For example, KF means it can be overclocked but has no graphics.
The Significance of ‘FMB’ in Intel CPUs
FMB stands for Flexible Motherboard. It’s not a common term in CPU names.
FMB refers to a type of CPU package. These chips can work with different motherboards. This makes them easier to use in many systems.
FMB CPUs are often found in business computers. They help companies save money. With FMB, one CPU type can fit in various computer models.
Intel doesn’t use FMB in its main product names. It’s more of a technical spec. Most users don’t need to worry about it when buying a CPU.
Technical Implications of ‘FMB’ on Performance and Compatibility
FMB on Intel CPUs affects processor speed and how well it works with other computer parts. This feature changes power use and processing ability in important ways.
Impact on Processor Performance
FMB allows Intel Core CPUs to run faster than normal. It boosts clock speeds above the usual limits. This means the CPU can do more work in less time.
FMB increases the power draw and heat output of the processor. The CPU needs better cooling to handle the extra heat. It may use more electricity too.
Some key benefits of FMB:
- Higher peak performance
- Faster task completion
- Better responsiveness
But there are trade-offs:
- More power used
- Extra heat created
- May reduce CPU lifespan if used a lot
Compatibility with Other Hardware Components
FMB puts extra stress on the motherboard and power supply. Not all systems can handle the increased power needs. Users need a strong power supply and good motherboard to use FMB safely.
FMB often works best with a separate graphics card. The extra power helps balance out high-performance GPUs. Systems with just built-in graphics may not see as much benefit.
Other parts to check for FMB use:
- CPU cooler (must handle extra heat)
- RAM (faster memory helps)
- Storage (SSDs can keep up with faster CPU)
Matching the right parts ensures the whole system runs well with FMB enabled. This gives the best mix of speed and stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Intel CPU model numbers use letter suffixes to show different features. These letters tell you about the processor’s abilities and what it’s made for.
What is the significance of the ‘F’ suffix in Intel processor models?
The ‘F’ suffix means the CPU does not have built-in graphics. You need a separate graphics card with these processors. They often cost less than models with integrated graphics.
How do the letter suffixes in Intel CPU model numbers relate to processor features?
Letter suffixes show specific features. ‘K’ means the CPU can be overclocked. ‘T’ indicates low power use. ‘H’ is for high-performance mobile processors. Each letter points to a unique trait.
Can you explain the meaning of ‘B’ in Intel CPU designations?
The ‘B’ suffix is not common. It stands for “Ball Grid Array” packaging. This type of CPU is soldered directly to the motherboard. It’s mostly used in small or thin devices.
What features are indicated by the ‘M’ suffix in Intel processor names?
The ‘M’ suffix was used for mobile processors in older Intel CPUs. It meant the chip was made for laptops. Now, Intel uses different letters like ‘U’ or ‘H’ for mobile chips.
How does Intel categorize their processor generations and performance?
Intel uses numbers to show generations. Higher numbers mean newer chips. The first digit often shows the generation. Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 show performance levels, with i9 being the top.
In what way do the various Intel processor suffixes affect computing capabilities?
Suffixes can mean big changes in what a CPU can do. ‘K’ chips let users boost speed. ‘F’ models need a separate graphics card. ‘U’ chips use less power but may not be as fast as others.