When your computer won’t play sound, it can be frustrating. One common error message is “no audio output device is installed.” This means Windows can’t find your speakers or headphones. To fix this, you might need to update drivers, check connections, or run the Windows audio troubleshooter.
Many things can cause this problem. Your sound card might not be working right. The drivers that help your computer talk to your speakers could be old or broken. Or, there might be a problem with Windows itself.
Don’t worry if you see this error. It’s usually easy to fix. We’ll show you some simple steps to get your sound working again. With a few clicks, you can often solve the problem and get back to enjoying your music or videos.
Troubleshooting “No Audio Output Device is Installed” Error
The dreaded “No Audio Output Device is Installed” error can bring your listening experience to a screeching halt. This error usually indicates that your computer can’t detect or communicate with your speakers or headphones. But don’t worry, here’s a troubleshooting guide to help you get your sound back:
1. Check Physical Connections
- Loose connections: Ensure your speakers or headphones are properly plugged into the correct audio jack (usually green for headphones/speakers).
- Try a different port: If you have multiple audio jacks, try plugging into a different one.
- Cable damage: Inspect the audio cable for any visible damage or fraying. Try a different cable if you have one.
2. Restart Your Computer
A simple restart can often resolve temporary glitches that might be causing the audio issue.
3. Update or Roll Back Audio Drivers
Outdated or corrupted audio drivers can cause sound problems.
- Update drivers: Go to your computer manufacturer’s website or your sound card manufacturer’s website (e.g., Realtek, Creative) and download the latest audio drivers for your model.
- Roll back drivers: If you recently updated your drivers, try rolling back to the previous version. This option is usually available in the Device Manager.
4. Run the Audio Troubleshooter
Windows has a built-in audio troubleshooter that can automatically diagnose and fix common sound problems.
- Open the troubleshooter: Right-click on the speaker icon in the system tray and select “Troubleshoot sound problems.”
- Follow the prompts: Follow the on-screen instructions to run the troubleshooter and apply any recommended fixes.
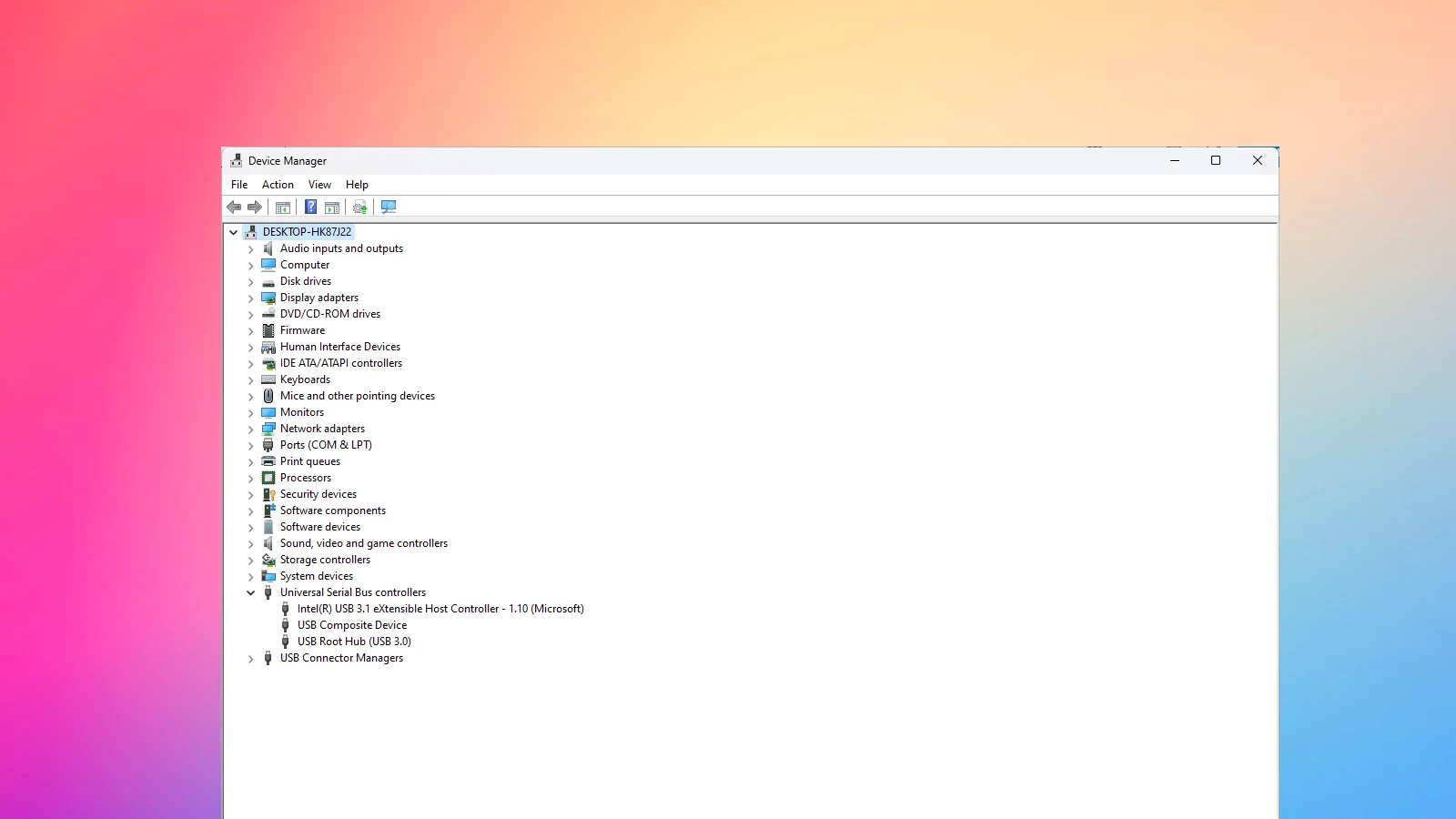
5. Check Device Manager
- Open Device Manager: Search for “Device Manager” in the Windows search bar and open it.
- Look for audio devices: Expand the “Sound, video and game controllers” category.
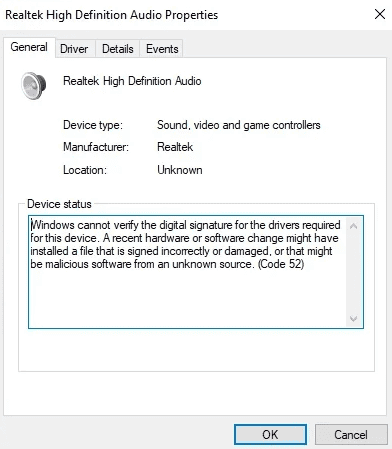
- Check for errors: Look for any devices with a yellow exclamation mark or a red X, which indicates a problem.
- Update or reinstall drivers: If you find any problematic devices, try updating or reinstalling their drivers.
6. Check Sound Settings
- Open Sound settings: Right-click on the speaker icon in the system tray and select “Open Sound settings.”
- Choose output device: Make sure the correct output device is selected (e.g., speakers, headphones).
- Test the sound: Click on “Test” to check if sound is playing through the selected device.
| Troubleshooting Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Check physical connections | Ensure proper connections and cable integrity |
| Restart your computer | Resolve temporary glitches |
| Update or roll back audio drivers | Address driver-related issues |
| Run the audio troubleshooter | Automatically diagnose and fix problems |
| Check Device Manager | Identify problematic audio devices |
| Check sound settings | Verify correct output device and test sound |
If you’ve tried these steps and still have no sound, you might have a more serious hardware issue. Consider seeking professional help from a qualified technician.
Additional Tips
- Disable audio enhancements: Some audio enhancements can interfere with sound output. Try disabling them in your sound card’s control panel.
- Check BIOS settings: In rare cases, the audio output might be disabled in the BIOS settings. Refer to your computer’s manual on how to access and check BIOS settings.
- System restore: If the problem started recently, try restoring your system to a point when the audio was working correctly.
Key Takeaways
- The error means Windows can’t find your speakers or headphones
- Updating drivers or running the audio troubleshooter can often fix the issue
- Most audio problems can be solved with simple steps
Understanding Audio Output Issues
Audio problems can be frustrating. They often stem from software glitches, driver issues, or hardware problems. Let’s explore the main causes and how to fix them.
Common Causes of Audio Problems
No sound on your computer can happen for many reasons. Outdated audio drivers are a frequent culprit. These drivers may stop working after a Windows update.
Hardware issues can also cause sound problems. A faulty sound card or loose cable connections might be to blame. Sometimes, the audio device gets disabled by accident.
Software settings can mute your audio too. The Windows audio service might stop running. Or your computer could be set to the wrong audio output device.
To fix these issues, start by checking your cables and connections. Make sure your speakers or headphones are plugged in correctly. Then, update your audio drivers. If that doesn’t work, try the built-in Windows troubleshooter.
Exploring the Device Manager
The Device Manager is a key tool for fixing audio issues. It lets you manage all the hardware on your computer, including sound devices.
To open Device Manager:
- Right-click the Start button
- Select “Device Manager” from the menu
Look for the “Sound, video and game controllers” section. Expand it to see your audio devices. If you see a yellow exclamation mark, that device has a problem.
To fix issues:
- Right-click the audio device
- Choose “Update driver” or “Uninstall device”
If you uninstall, restart your computer. Windows will try to reinstall the driver automatically.
Updating drivers through Device Manager can often solve audio problems. If not, you may need to download drivers from your computer manufacturer’s website.
Using System Utilities for Troubleshooting
Windows has built-in tools to help fix audio problems. The audio troubleshooter is a good place to start.
To run the audio troubleshooter:
- Go to Settings > System > Troubleshoot
- Click “Other troubleshooters”
- Find “Playing Audio” and click “Run”
The troubleshooter will check for common problems and try to fix them automatically.
Another useful tool is the DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management) command. It can repair Windows system files that might be causing audio issues.
To use DISM:
- Open Command Prompt as administrator
- Type “DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth”
- Press Enter and wait for the process to finish
If these tools don’t work, you can try a System Restore. This will roll back your system to a point when the audio was working. Remember to create restore points regularly to make this option more useful.