Digital Rights Management (DRM) is an essential technology that safeguards copyrighted content—such as movies, music, ebooks, and software—against unauthorized access or distribution. It plays a crucial role in enabling seamless playback on streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video, ensuring that only authorized users can access premium content.
When DRM is disabled, users may encounter playback errors, content loading issues, or restricted access to certain media. While most major browsers—including Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari—support DRM, it often requires manual activation. Fortunately, enabling DRM is a straightforward process across different devices and platforms. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to turn on DRM in your browser, media players, streaming services, and more, so you can enjoy uninterrupted access to your favorite content.
1. Enable DRM in Web Browsers
Some websites and streaming services require DRM to play protected content. Here’s how to enable DRM in popular web browsers:
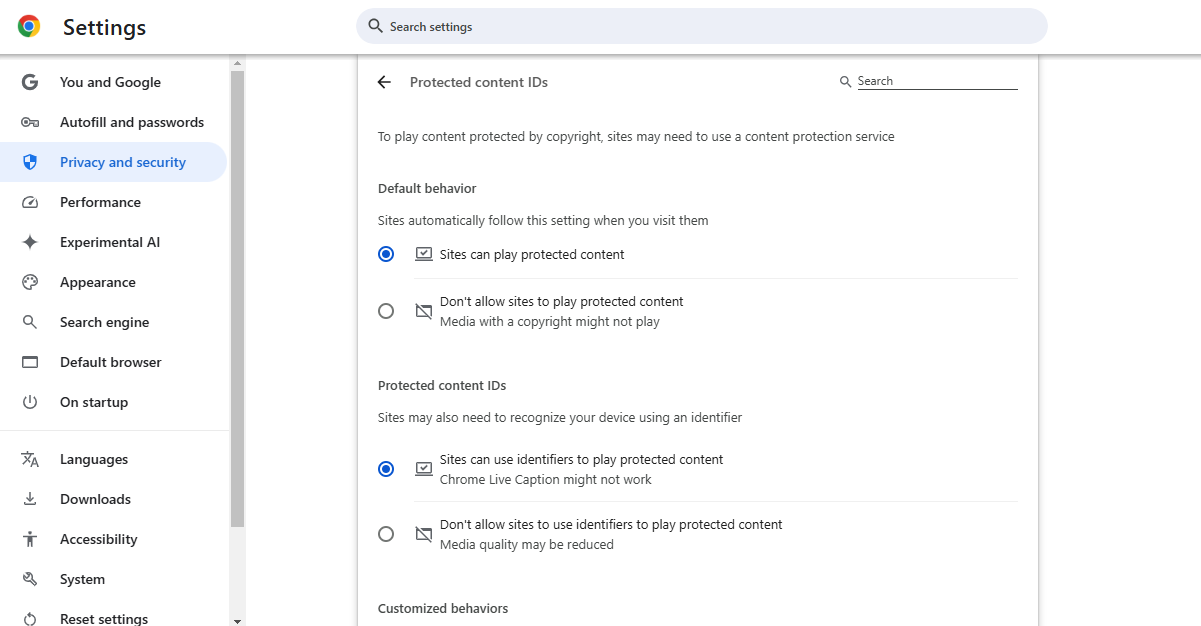
Google Chrome
- Open Chrome and go to
chrome://settings/content/protectedContent. - Make sure both options under Protected Content are turned on:
- “Sites can play protected content.”
- “Sites can use identifiers to play protected content.”
Mozilla Firefox
- Open Firefox and go to
about:preferences#general. - Scroll down to Digital Rights Management (DRM) Content.
- Check the box “Play DRM-controlled content.”
- If prompted, install the Widevine Content Decryption Module.
Microsoft Edge
- Open Edge and type
edge://settings/content/protectedContentin the address bar. - Enable “Allow sites to play protected content.”
- Restart the browser to apply the changes.
Safari (Mac)
- Open Safari and go to Preferences > Websites > Plug-ins.
- Ensure “Enable DRM Content” or “Enable Widevine” is checked.
- Restart Safari.
2. Enable DRM in Streaming Services
Some streaming services like Netflix, Disney+, and Amazon Prime require DRM to stream content.
Netflix
- Netflix automatically enables DRM if your browser supports it.
- If you experience issues, ensure Widevine DRM (for Chrome/Firefox) or PlayReady DRM (for Edge) is enabled.
Amazon Prime Video
- Works on browsers that support DRM (Chrome, Edge, Safari, and Firefox with Widevine enabled).
- If using the app, ensure it’s updated to the latest version.
Disney+
- Requires HDCP 2.2 (for 4K playback) on connected displays.
- Use a supported browser with DRM enabled.
3. Enable DRM on Android & iOS
Some apps and content providers require DRM to function correctly on mobile devices.
Android
- Go to Settings > Apps & Notifications.
- Find the streaming app (e.g., Netflix, Disney+).
- Ensure the app is updated.
- Some content requires Widevine DRM, which is automatically enabled on certified devices.
iOS (iPhone & iPad)
- Apple uses FairPlay DRM by default for iTunes and Apple TV content.
- If DRM-protected content isn’t playing, update the app or check if the HDCP-compliant display is used.
4. Enable DRM in Media Players
Certain media players require DRM for playback.
VLC Player (Limited DRM Support)
- VLC does not support DRM-protected content.
- Use official apps for DRM-restricted content (e.g., Netflix app instead of playing DRM content in VLC).
Windows Media Player
- Open Windows Media Player.
- Go to Tools > Options > Privacy.
- Enable Download usage rights automatically.
Apple Music & iTunes
- Apple Music uses FairPlay DRM.
- DRM is enabled automatically when downloading or streaming protected content.
5. Enable DRM on Smart TVs & Consoles
Some DRM-protected content requires HDCP-compliant devices.
Smart TVs
- Ensure HDCP 2.2 compatibility for 4K streaming.
- Check for software updates in the TV settings.
PlayStation & Xbox
- Streaming apps (Netflix, Prime Video, etc.) require DRM-enabled settings.
- Ensure your HDMI cable supports HDCP.
Final Thoughts
Turning on DRM ensures you can access legally protected content while preventing unauthorized use. If you experience issues, check for browser updates, device certification (Widevine, PlayReady, FairPlay), and HDCP compatibility.
Key Takeaways
- DRM settings can be found in browser settings under Protected Content or Site Settings
- Modern browsers include built-in DRM support for streaming services
- Users can quickly fix streaming issues by enabling DRM features
Enabling DRM on Popular Browsers
Digital Rights Management (DRM) settings need to be correctly configured in web browsers to play protected content from streaming services. The steps differ between Chrome, Firefox, and Edge browsers.
Chrome: Adjusting Content Settings
To enable DRM in Chrome, users must access the browser settings menu by clicking the three dots in the top-right corner.
Navigate to Settings > Privacy and Security > Site Settings > Additional Content Settings > Protected Content.
Enable these two options:
- Allow sites to play protected content (recommended)
- Enable the Widevine Content Decryption Module
This setup lets Chrome handle DRM-protected videos and music from streaming platforms without interruption.
Firefox: Managing DRM and Content Decryption
Firefox’s DRM settings are straightforward to configure. Open the Firefox menu and select Settings.
Scroll down to the Digital Rights Management (DRM) section in the General settings tab. Check the box labeled “Play DRM-controlled content.”
Firefox will download and install the required content decryption modules automatically. A browser restart may be needed for changes to take effect.
Microsoft Edge: Configuring DRM Settings
Edge uses the Widevine Content Decryption Module for DRM playback. Access Edge settings through the three-dot menu.
Navigate to:
- Settings > Cookies and Site Permissions
- Protected Content and Downloads
- Toggle on “Allow sites to play protected content”
Edge typically enables DRM by default. If playback issues occur, verify these settings are correctly configured.
Troubleshooting and Advanced DRM Considerations
Digital Rights Management systems help protect streaming content but can sometimes present technical challenges. Advanced settings and proper configuration ensure smooth playback across major platforms.
Resolving DRM Playback Issues
Browser extensions can interfere with DRM functionality on streaming platforms like Netflix and Hulu. Disabling all extensions temporarily helps identify problematic add-ons.
If DRM errors persist in Chrome or Firefox, users should:
- Clear browser cache and cookies
- Update the browser to the latest version
- Check if Widevine Content Decryption Module (CDM) is installed correctly
- Verify the streaming service account has proper permissions
Some antivirus software can block CDM components. Temporarily disabling security software can help identify if it’s causing interference.
Understanding the Impact of DRM Software
Different browsers use specific DRM technologies: Chrome and Edge rely on Google Widevine, while Firefox supports multiple CDM types.
Key DRM components include:
- Widevine CDM for Chrome and Edge
- PlayReady for Microsoft platforms
- HTML5 video protection layers
- Content encryption protocols
Each streaming platform implements unique DRM requirements. Amazon Prime Video might need different settings than Netflix or Hulu.
Content Protection and Intellectual Property
DRM technology safeguards digital content through encryption and access control. Modern browsers include built-in content protection features that work with streaming services.
Protected content types include:
- HD video streams
- Premium audio content
- Downloaded media files
- Live broadcast streams
Users must accept DRM terms before accessing protected content. Copyright holders can track and control content distribution through DRM systems.
Internet connection quality affects DRM authentication. A stable network helps prevent playback interruptions and licensing errors.







