In today’s digital age, understanding the different types of USB connectors is essential for anyone who uses technology. The Universal Serial Bus (USB) has evolved significantly since its introduction and has become a fundamental component for connecting modern devices. The original USB-A connector, known for its flat and rectangular shape, paved the way for a wide range of USB styles. As technology has progressed, the demand for various connectors has also increased. The USB-B connector, with its square design, is commonly found in peripherals like printers.
Meanwhile, the introduction of USB-C has brought features like a reversible design, high-speed data transfer, and improved power delivery. USB connectors serve many purposes, from charging gadgets to transferring data between devices. Additionally, the mini and micro variations of USB connectors provide smaller options for portable devices. Understanding the interoperability of these connectors is vital for selecting the appropriate type for a particular application. Choosing the right cable involves recognizing not only the physical differences but also the technical specifications and functionalities of each USB type.

Decoding USB Types: A Comprehensive Guide
USB is everywhere. It’s how we connect our phones, cameras, and countless other devices. But have you ever wondered about the different types of USB connectors? This guide breaks down the most common types, their uses, and their pros and cons.
USB-A
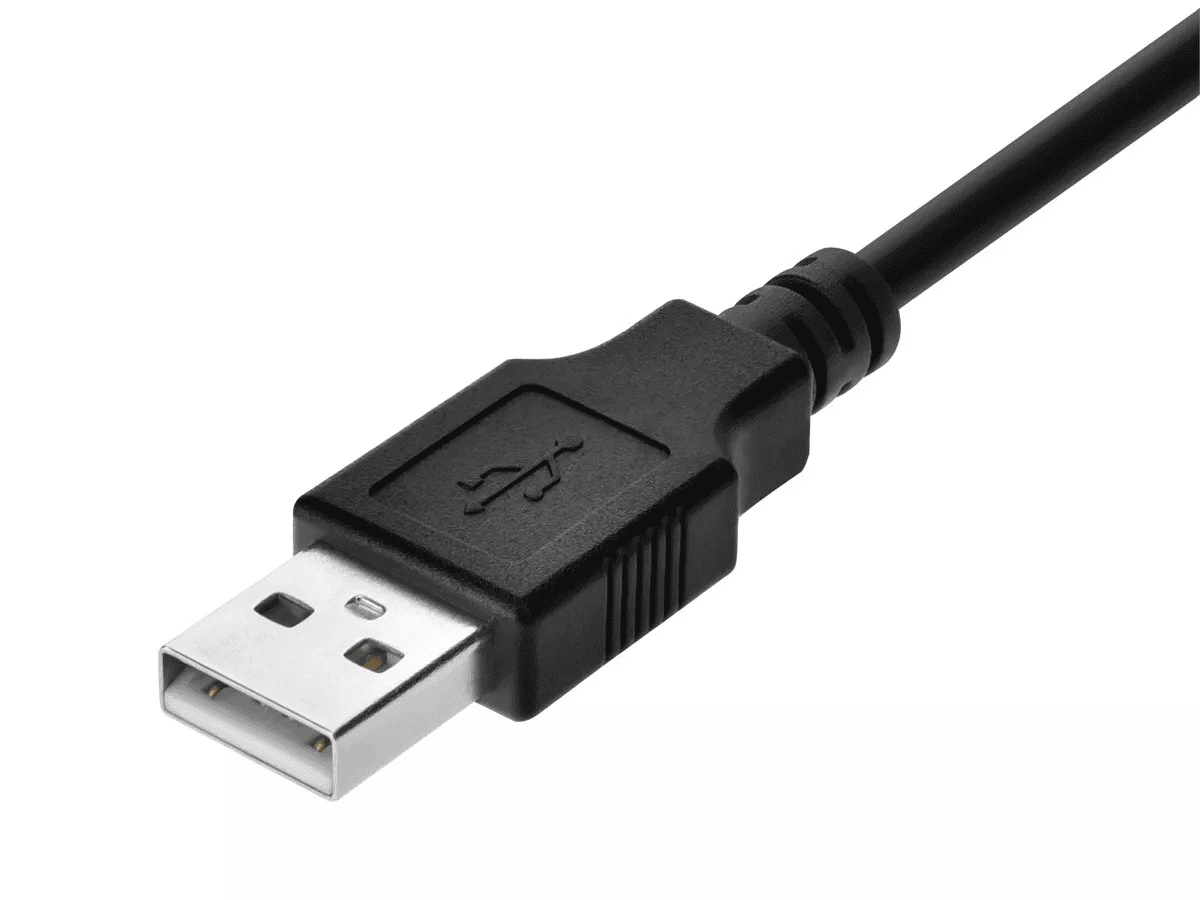

This is the classic, rectangular USB connector. It’s what you probably picture when you think of USB.
- Pros: Widely compatible, found on many devices.
- Cons: Can only be plugged in one way (and it’s often the wrong way the first time!).
- Common Uses: Computers, laptops, game consoles, TVs.
USB-B
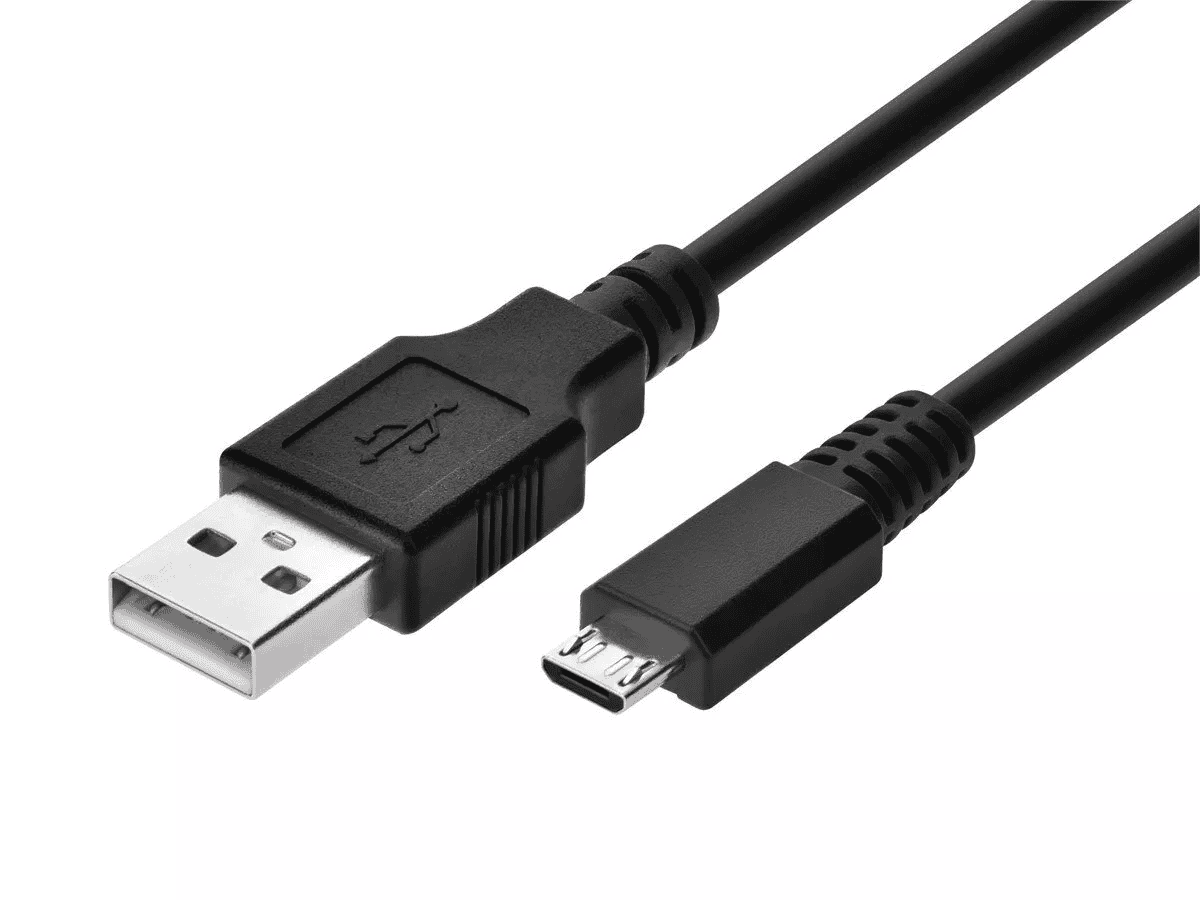

This square-ish connector is less common than USB-A.
- Pros: More durable than USB-A, often used for larger devices.
- Cons: Not as widely used as USB-A.
- Common Uses: Printers, scanners, external hard drives.
USB-C

This is the newest type of USB connector. It’s small, reversible, and can handle high data transfer speeds.
- Pros: Fast, versatile, can carry power and video signals.
- Cons: Not as widely compatible as USB-A (yet!).
- Common Uses: Newer smartphones, laptops, tablets, chargers.
Mini-USB

This smaller connector was popular on older devices.
- Pros: Smaller than USB-A, good for portable devices.
- Cons: Less durable than other types, not as common anymore.
- Common Uses: Older cameras, MP3 players.
Micro-USB
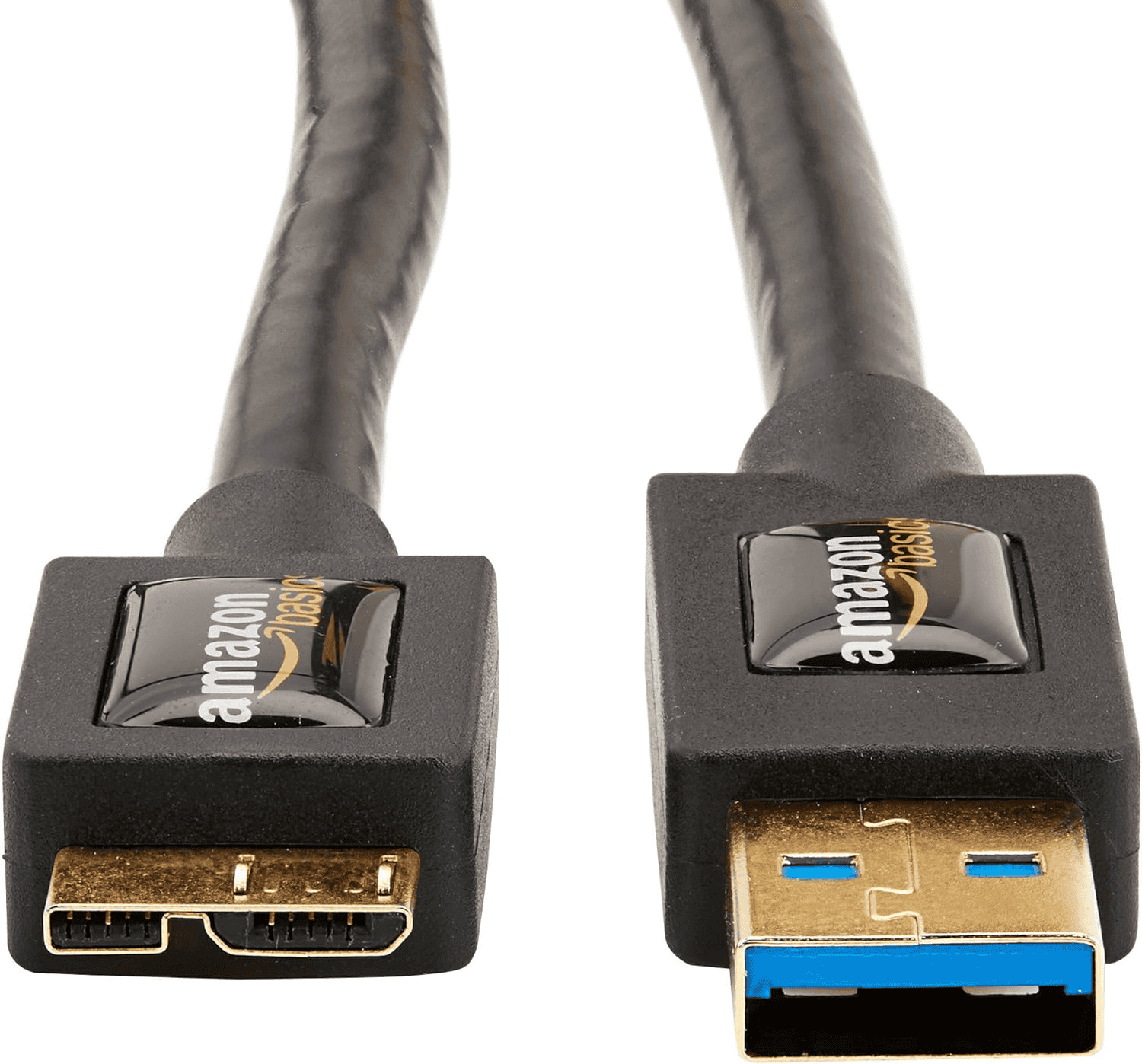
This even smaller connector was also common on older devices.
- Pros: Very small, good for compact devices.
- Cons: Less durable than other types, easily damaged.
- Common Uses: Older smartphones, tablets.
Lightning

This connector is used on Apple devices.
- Pros: Small, durable, reversible.
- Cons: Only compatible with Apple devices.
- Common Uses: iPhones, iPads, AirPods.
Understanding USB Generations
Besides the connector type, USB also has different generations. These refer to data transfer speeds.
- USB 1.x: The oldest and slowest.
- USB 2.0: Faster than USB 1.x, still common.
- USB 3.x: Much faster than USB 2.0, often blue in color.
- USB4: The newest and fastest, compatible with USB-C.
The Future of USB
USB-C is becoming the standard. It’s likely to replace all other types eventually. It’s fast, versatile, and can handle the demands of modern devices.
Understanding the different USB types can help you choose the right cables and devices. While USB-A is still common, USB-C is the future. It offers faster speeds and greater versatility.
Key Takeaways
- USB technology is integral for device connectivity and comes in various shapes and forms.
- The right USB connector type is essential for the intended application, considering both physical compatibility and technical needs.
- Evolution of USB from Type-A to USB-C reflects advancements in data transfer speed and power delivery.
Understanding USB Technology
Universal Serial Bus (USB) technology is central to data transfer and device charging. Now, let’s break down the intricacies of USB technology.
Evolution of USB Standards
USB was introduced in the mid-1990s with USB 1.0, evolving to USB 1.1 which standardized data transfer rates. The speed increased with USB 2.0, and even more so with USB 3.x series, culminating in USB 4.0, which coexists with Thunderbolt 4 for maximum transfer speeds.
Types of USB Connectors
There are several USB connector types:
- USB-A: The original, rectangular shape.
- USB-B: Less common, squarer shape, often used with printers.
- Mini-USB and Micro-USB: Smaller connectors for various devices.
- USB-C: Reversible and used for a broad range of devices.
USB Functionality and Use Cases
USB facilitates both data transfer and power delivery. It connects a multitude of devices including computers, smartphones, tablets, and peripheral devices like printers and storage the devices.
Advanced USB Features
USB Power Delivery (PD) enhances charging capabilities, while SuperSpeed USB denotes higher data transfer rates. USB On-The-Go (OTG) allows USB devices to connect without needing a PC intermediary.
Device Compatibility and Interconnectivity
USB standards ensure backward compatibility, meaning newer versions work with older ports. However, speed and power are limited by the older technology’s capabilities.
Future of USB Technology
The USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) governs USB standards, working with manufacturers like Anker to drive advancements in USB technology. Environmental considerations are influencing packaging and product design.







