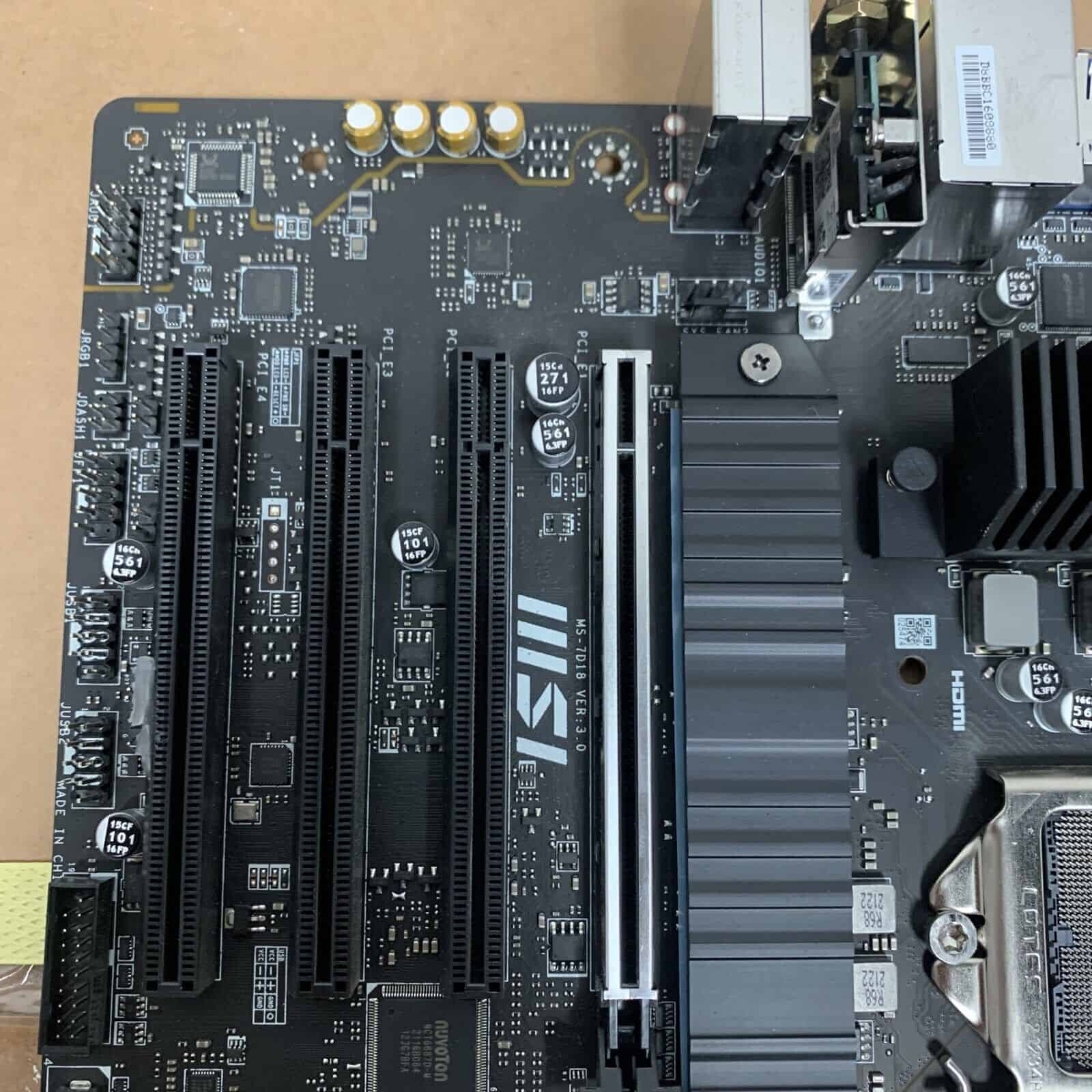
Expansion slots on a motherboard are narrow sockets where additional circuit boards, called expansion cards, can be inserted. These slots allow users to enhance their computer’s capabilities by adding features that the motherboard may not have, such as improved graphics, sound, or network capabilities. Various types of cards, including video cards, sound cards, and network cards, can be accommodated in these slots.
Over the years, the design and technology of expansion slots have evolved from industry-standard architectures like PCI to more advanced versions like PCI Express, which is commonly found in modern computers and supports faster data transfer rates. It’s important to know the type of expansion slots your motherboard has when planning to upgrade your computer system.
Understanding Expansion Slots on Your Motherboard
Motherboards are the backbone of our computers. On these circuit boards, we find the essential components that make a computer function: the CPU, RAM, storage connectors, and more. Another vital part of the motherboard is its expansion slots. Let’s dive into what these slots do and the various types available.
What Exactly Is an Expansion Slot?
An expansion slot serves as a dedicated port on your motherboard designed to plug in expansion cards. These cards add extra features and capabilities to your computer, expanding its potential. Some commonly used expansion cards include:
- Graphics Cards: For better visuals in games and other demanding programs.
- Sound Cards: Upgrading your computer’s audio capabilities.
- Network Cards: Adding wired (Ethernet) or wireless (Wi-Fi) networking options
- Capture Cards: Connecting external video sources like game consoles or cameras.
Popular Types of Expansion Slots
Expansion slots have changed over the years. Here’s a breakdown of some common types you might find on your motherboard:
| Slot Type | Brief Description | Typical Usage |
|---|---|---|
| PCI | An older, standard slot type. | Sound cards, network cards, and other less-demanding expansions. |
| PCIe | The most modern standard – comes in different lengths/speeds (x1, x4, x8, x16) | Demanding cards like graphics cards, fast storage drives, etc. |
| AGP | A dedicated graphics card slot, outdated on most newer motherboards. | Older graphics cards. |
Why Use Expansion Slots?
Expansion slots are what make PCs highly customizable. Here’s why they’re important:
- Upgradability: Instead of buying a whole new computer, you can enhance your existing system’s performance by swapping out or adding cards in these slots.
- Tailored Functionality: Expansion cards let you add specific features you need, such as powerful graphics for gaming or professional-grade audio for music production.

Key Takeaways
- Expansion slots on a motherboard allow for the addition of expansion cards.
- They enable customization and enhancement of a computer’s functionality.
- Different types of slots support varying data transfer speeds and card sizes.
Understanding Motherboard Expansion Slots
Expansion slots are vital for adding new hardware to a computer, allowing upgrades like enhanced graphics or improved sound.
Types of Expansion Slots
Motherboards come with various slots for connecting extra components. The most common types are:
- PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect): An older slot type for network cards and other features.
- AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port): Used mainly for video cards, now mostly replaced.
- PCIe (PCI Express): The latest and most used standard, which comes in different sizes like x1, x4, x8, and x16.
Each type fits different cards and serves distinct purposes.
Functionality and Compatibility
Expansion slots let users upgrade their computer’s functionality by adding hardware like sound cards, graphics cards, and network cards. Before adding a card, it’s important to ensure that the slot type matches it. For example:
- A sound card usually fits into a PCIe x1 slot.
- A graphics card needs a PCIe x16 slot for best performance.
This compatibility implies the slot and card can work together.
Performance and Speed
The performance and speed of an expansion card are tied to the slot type. PCIe slots are faster than PCI or AGP slots due to more recent technology. For example:
- PCIe x1 slots offer up to 1 GB/s per lane.
- PCIe x16 slots can give much higher speeds, important for high-demand graphics cards.
The right slot helps a card perform at its best.
Enhancing Computer Capabilities with Expansion Cards
Motherboard expansion slots are key to improving and customizing a computer. They let users add new features and boost computer power with different cards.
Common Expansion Cards and Their Purposes
Graphics Card (GPU): This card makes games and videos look better. It can help with smoother visuals and faster video editing.
- Benefits: Sharper images and fluid video play
Sound Card: Improves audio for music and games. Gives better sound than built-in options.
- Benefits: Clearer sound and enhanced audio tuning
Network Card: Connects computers to networks. Useful for fast internet and network access.
- Benefits: Reliable internet connection and fast network response
Solid State Drives (SSDs): Speeds up data access. SSDs are faster than hard drives.
- Benefits: Quick boot times and fast file transfers
Wi-Fi Adapters: Gives wireless internet. Useful for computers without built-in Wi-Fi.
- Benefits: Internet access without wires
RAID Controllers: These manage many hard drives. They help with data safety and speed.
- Benefits: Protects data and can speed up access
Table 1: Expansion Card Types and Their Benefits
| Expansion Card Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Graphics Card (GPU) | Enhances visual performance | Better game and video quality |
| Sound Card | Upgrades audio capabilities | Superior sound clarity |
| Network Card | Provides network connectivity | Quick and smooth internet access |
| SSD | Enhances storage speed | Faster system and file access |
| Wi-Fi Adapter | Adds wireless connectivity | Easy and tidy internet setup |
| RAID Controller | Manages multiple storage devices | Increases data reliability and speed |
Choosing the Right Expansion Card for Your Needs
The right card matches the computer’s slots. Slots like PCI, AGP, and PCIe determine compatibility. Here’s how to choose well:
- Check Compatibility: Verify that the card fits the motherboard’s slot type.
- Understand Needs: Pick a card based on what the computer will do. Games need a good GPU. For music, consider a sound card.
- Consider Upgrades: Plan for the future. A card that can handle upcoming needs is wise.
By adding the right cards, computers can do more and work better. Remember to match cards with the motherboard’s abilities. This will improve your computer’s functions and maybe even its longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Expansion slots are vital for adding new features and boosting a computer’s abilities. Here are some common questions to help you understand their role.
What functions do expansion slots perform in a motherboard?
They let you add more cards to a computer. This way, a motherboard gets new or improved features.
Which types of expansion slots are commonly found on motherboards?
You’ll see PCI Express, PCI-X, and AGP slots in most motherboards. Each one fits different cards.
Can you provide examples of peripherals that utilize expansion slots?
Expansion slots can hold sound cards, graphics cards, and network cards. They link these devices to the system.
How does a PCI expansion slot differ from other types of slots?
PCI slots connect different hardware to a computer. They are not as fast as PCI Express slots, which are for newer and faster devices.
What role does an expansion bus slot play in the functionality of a motherboard?
An expansion bus slot lets add-on cards talk to the motherboard. It is part of how a computer works.
Why are AGP expansion slots important, and how are they distinct?
AGP slots are for graphics cards. They give better video quality and are different from PCI slots.







