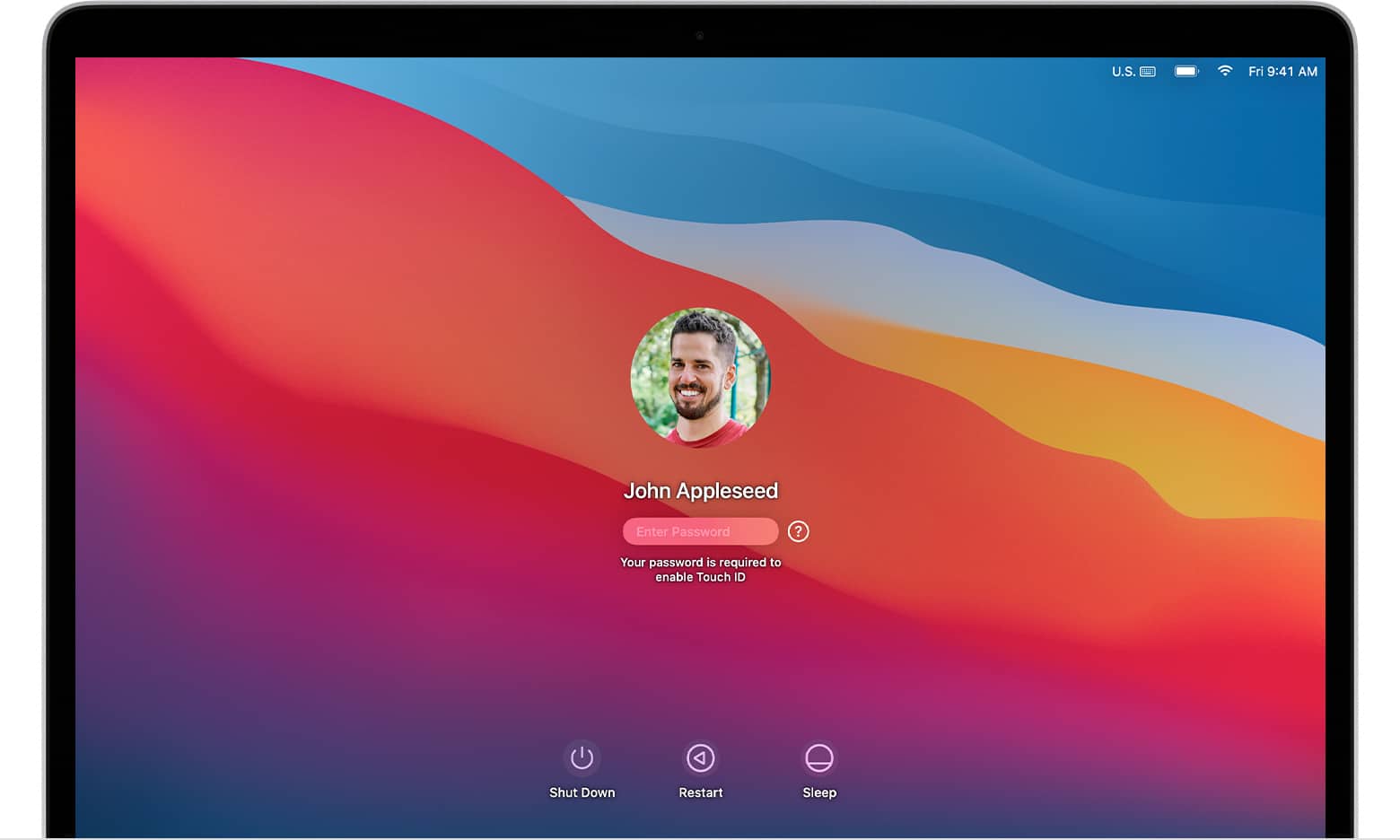
Creating strong passwords is essential for keeping your online accounts secure. Use unique and difficult-to-guess passwords to protect your personal information from cyberattacks. Avoid using common words, names, birthdates, or simple patterns. Consider using a password manager to create and store complex passwords for each account, making it easier to manage multiple passwords.
Keeping a list of your passwords on paper can also work; just make sure to store it safely. Always avoid using the same password for multiple accounts. If one account gets hacked, all your other accounts could be at risk. Keep a close eye on your password security to keep your data safe.
Strengthening Your Digital Defenses
In today’s digital age, our lives are increasingly intertwined with online accounts and sensitive information. Strong passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access and potential identity theft. Let’s explore some essential tips to fortify your password security and safeguard your digital presence.
Creating Strong Passwords: The Basics
- Length Matters: Aim for passwords that are at least 12 characters long. Longer passwords are exponentially harder to crack.
- Complexity is Key: Combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols for a robust password.
- Avoid Personal Information: Refrain from using easily guessable information like names, birthdays, or pet names.
- Don’t Reuse Passwords: Each account should have a unique password to prevent a domino effect if one is compromised.
- Use a Passphrase: Instead of a single word, create a memorable phrase with random words and characters.
Password Management Tools: Your Digital Vault
- Password Managers: These tools securely store and generate complex passwords, eliminating the need to remember them all.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step, like a code sent to your phone.
- Biometric Authentication: Utilize fingerprint or facial recognition for convenient and secure logins on supported devices.
Additional Tips for Enhanced Security
- Regularly Update Passwords: Don’t let your passwords gather dust. Change them periodically, especially for sensitive accounts.
- Be Wary of Phishing Scams: Avoid clicking on suspicious links or sharing sensitive information in unsolicited emails or messages.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your operating systems and applications to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use Strong Security Questions: Choose questions that are difficult for others to guess and provide unpredictable answers.
- Monitor Your Accounts: Keep an eye on your bank and credit card statements for any unauthorized activity.
Table: Password Do’s and Don’ts
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Use a mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols. | Use easily guessable information like names or birthdays. |
| Create long and complex passwords. | Reuse the same password for multiple accounts. |
| Utilize a password manager. | Share your passwords with anyone. |
| Enable two-factor authentication. | Click on suspicious links or attachments. |
| Regularly update your passwords. | Use public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions. |
Key Takeaways
- Unique passwords protect against cyberattacks
- Password managers help manage strong passwords
- Do not reuse passwords across accounts
Fundamentals of Password Security
Secure passwords are crucial in protecting against cyber threats and unauthorized access. Weak passwords expose users to risks such as identity theft and data breaches.
Understanding the Importance of Strong Passwords
Strong passwords serve as a frontline defense against unauthorized access. They protect sensitive information from hackers and cybercriminals. Without a strong password, personal and financial data can be easily compromised. Cybersecurity measures depend heavily on the strength of your passwords.
Short and simple passwords are vulnerable to brute force attacks and dictionary attacks. A good password reduces the chance of being guessed, safeguarding against common hacking methods.
The Anatomy of a Strong Password
A strong password includes a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. It should be at least 16 characters long. This complexity makes it harder for cybercriminals to crack.
For added security, passwords should avoid common words and personal information like names or dates. Using random character combinations and changing passwords regularly helps protect against security breaches.
Using a passphrase can also create a strong password. Choose random words and combine them with symbols or numbers. This enhances the difficulty for hackers to guess.
Risks Associated with Weak Passwords
Weak passwords greatly increase the risk of data breaches and identity theft. Cybercriminals use various tactics like phishing and social engineering to exploit weak passwords.
Reusing passwords across multiple accounts can lead to widespread compromises if one account gets hacked. Weak passwords can also facilitate malware attacks and unauthorized access.
Insecure passwords like common words or short phrases are easy for hackers to guess. This exposes users to threats that compromise their personal and financial information, leading to significant harm.
FAQs
These questions cover practical tips and strategies for creating and managing strong and secure passwords.
How can one create a strong and secure password?
Use a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Make sure the password is at least 12-16 characters long. Avoid common words and simple patterns.
What are some strategies for employees to maintain password security?
Change passwords regularly and avoid using the same password for multiple accounts. Use two-factor authentication when possible. Don’t share passwords with anyone.
What are the recommended methods for securely managing passwords?
Use a password manager to store and generate passwords. Keep backups of passwords in a secure place. Regularly update the password manager.
What techniques can be used to create passwords that are easy to remember yet secure?
Create a phrase with random words. Use a combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information like names or birthdays.
What constitutes a strong password in current cybersecurity practices?
A strong password is at least 16 characters long. It includes a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. It avoids using common words or patterns like “1234” or “password”.
What are advanced practices for enhancing password security?
Enable multi-factor authentication. Monitor accounts for unusual activity. Use biometric authentication where possible. Regularly audit and update passwords to ensure they remain secure.