Managing a computer’s energy consumption and performance is important. Windows power plan settings help with this. They can be adjusted for better battery life or system performance. This is especially useful for laptop users who switch between being plugged in and running on battery power. In Windows 10 and Windows 11, you can easily access and change power plan settings through the System Settings or the Control Panel. Power plans help manage how your computer uses energy, balancing performance and battery life. You can choose pre-set plans or create a custom plan to match your specific needs.
This guide provides an overview of Windows power plans, their types, how to access them, and tips for optimizing your power settings. Changing power plan settings lets you define how your computer handles different power states like sleeping or screen dimming durations. This affects the device’s performance and energy efficiency. Power plans like Balanced, Power Saver, and High Performance suit different needs, and advanced settings offer further customization for specific hardware and system components, tailoring the computer’s operations to your specific needs.
Managing Power Usage with Windows Power Plans
Understanding Power Plans
Windows power plans are collections of settings that control how your computer uses energy. These plans balance performance and power consumption, letting you choose what matters most.
Types of Power Plans
| Power Plan | Description | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Balanced | Offers a middle ground between performance and energy efficiency. | Everyday use, general tasks |
| Power Saver | Prioritizes battery life over performance. | Laptops, devices used on battery for extended periods |
| High Performance | Maximizes performance at the cost of higher energy consumption. | Gaming, demanding tasks, editing software |
| Ultimate Performance | Pushes performance to the limit, but significantly increases energy consumption. (Not available on all devices) | Workstations, high-performance computing |
| Custom | Allows you to create a personalized power plan by adjusting individual settings. | Fine-tuning power usage based on specific needs |
Accessing Power Plan Settings
- Open Control Panel: Search for “Control Panel” in the Start menu and open it.
- Navigate to Power Options: Click on “Hardware and Sound,” then “Power Options.”
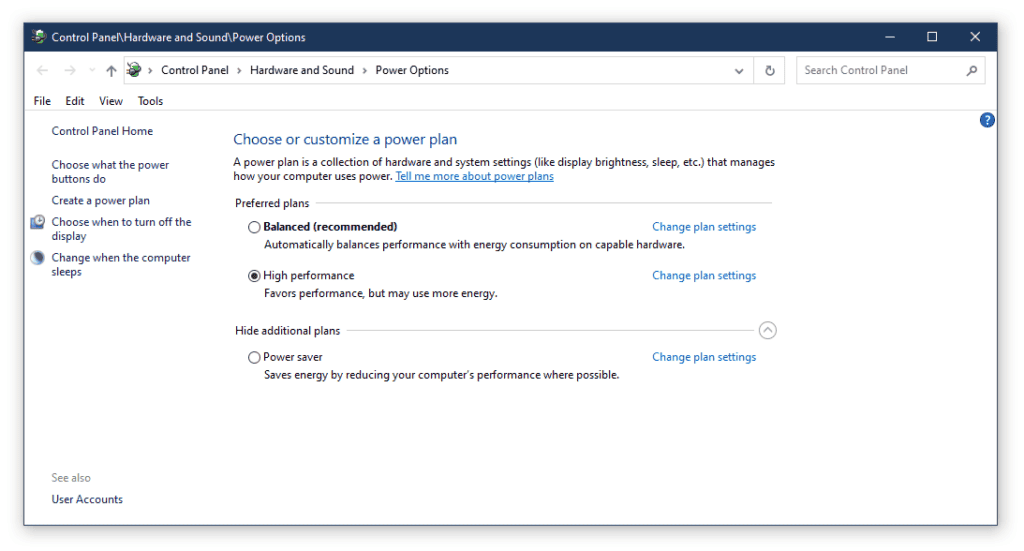
- Choose a Power Plan: Select the plan that suits your needs from the available options.
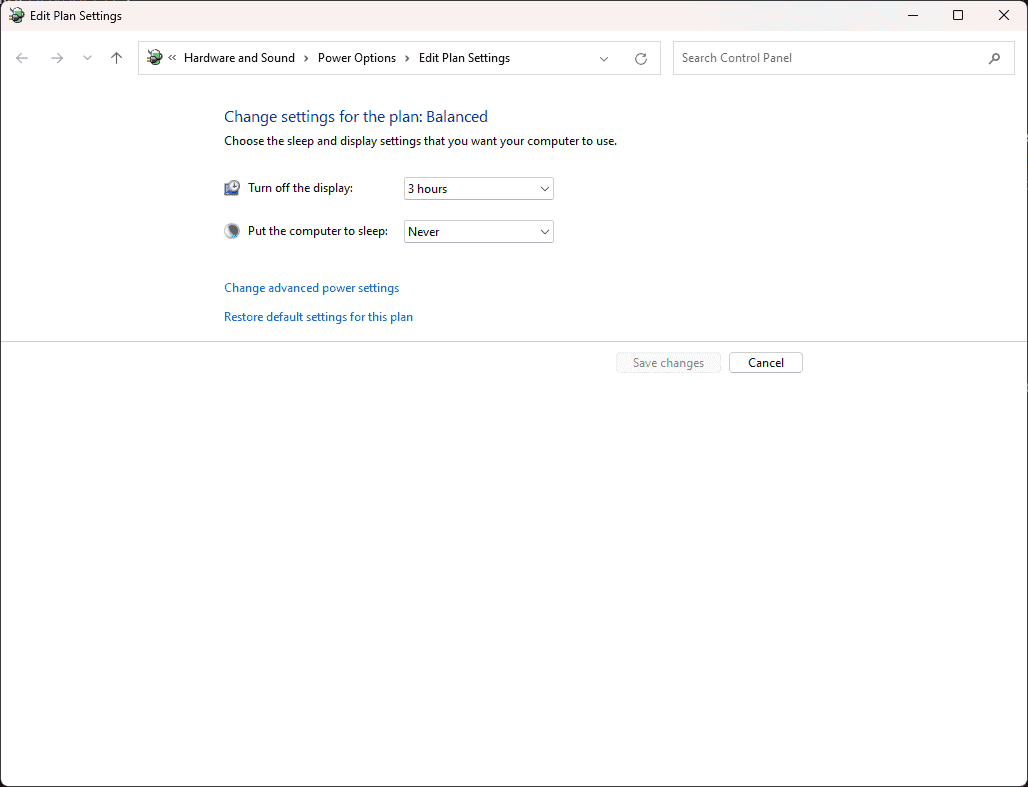
- Customize Plan Settings: Click “Change plan settings” next to your chosen plan to adjust individual settings like display timeout, sleep mode, and processor power management.
Additional Tips
- Create multiple power plans for different situations (e.g., one for work, one for gaming).
- Experiment with different settings to find the right balance between performance and battery life.
- Consider using the “Power Saver” plan when your battery is low.
- If you experience performance issues, try the “High Performance” or “Ultimate Performance” plan.
Key Takeaways
- Power plan settings manage a computer’s energy consumption and performance balance.
- Users can customize how their system responds to different power states.
- Balanced, Power Saver, and High Performance are the primary power plans available.
Understanding Power Plans in Windows
Windows Operating System incorporates power plans to manage how computers use energy. These settings are crucial for optimizing performance and extending battery life on portable devices.
Basic Power Plan Types
Windows offers several predefined power plans designed to meet different needs:
- Balanced: Automatically balances performance with energy consumption.
- Power Saver: Reduces computer performance to save energy.
- High Performance: Maximizes system performance at the cost of higher energy consumption.
- Ultimate Performance: Only available on certain systems, this plan is designed to eliminate micro-latencies and is intended for high-end PCs.
Customizing Power Plan Settings
Users can customize their power plans by adjusting a variety of settings:
- Screen and Sleep Settings: Determine when the display turns off and when the computer goes to sleep.
- Processor Power Management: Adjusts the maximum and minimum processor state.
- Hard Disk: Sets the idle period before the hard disk turns off.
- Wireless Adapter Settings: Manages power-saving mode for wireless adapters.
Advanced Power Settings
Advanced power settings allow users to finely tune hardware and system behavior:
- Desktop Background Settings: Specifies when the slideshow is paused.
- USB Settings: Manages USB selective suspend settings.
- PCI Express: Adjusts the link state power management policy.
- Battery Settings: Alters actions taken when the battery reaches critical levels.
Managing Power Plans
To manage these power plans, users access options through the Control Panel or by right-clicking the battery/energy icon in the system tray. One can switch between existing plans, create custom schemes, and select the default active power scheme. Advanced users can even alter power settings via command prompt using specific GUIDs associated with each plan.