Stress testing your CPU is crucial for assessing system stability and performance. AIDA64 offers a powerful tool for this purpose. The AIDA64 Stability Test puts your CPU under maximum load to uncover potential weaknesses or instabilities.
This process helps identify issues that might lead to crashes or unexpected behavior during everyday use. It’s particularly useful for those who have overclocked their CPUs or want to ensure their cooling solutions are adequate. AIDA64 allows users to stress individual components or run a full system test.
Running a CPU stress test with AIDA64 is straightforward. Users can select specific stress options like CPU, FPU, cache, or memory to target different aspects of their system’s performance. The software provides real-time monitoring of temperatures, clock speeds, and other vital statistics during the test.
How to Stress Test Your CPU with AIDA64
What is Stress Testing?
Stress testing pushes your CPU to its limits. It helps you check for stability and identify potential problems. These problems could be overheating or instability under heavy loads.
Why Stress Test Your CPU?
- System Stability: Ensure your computer can handle demanding tasks. This is important for gaming, video editing, and other resource-intensive activities.
- Overclocking: If you overclock your CPU, stress testing is essential. It confirms your overclock is stable.
- Cooling Performance: Check if your CPU cooler is working effectively.
- Identifying Potential Issues: Detect problems that might not appear during normal use.
What is AIDA64?
AIDA64 is a system information and diagnostics tool. It includes a stress test feature. This feature puts a heavy load on your CPU and other components.
Preparing for the Stress Test
Before you start, do these things:
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Close any programs running in the background. This ensures the stress test focuses solely on your CPU.
- Monitor Temperatures: Have a temperature monitoring tool open. This lets you watch your CPU temperatures during the test. HWMonitor or Core Temp are good options.
Step-by-Step Guide to Stress Testing with AIDA64
- Download and Install AIDA64: Download AIDA64 from the official website and install it. There is a trial version available.
- Open AIDA64: Launch the program.
- Start the System Stability Test: Go to Tools > System Stability Test.
- Select Stress Test Options: You will see various options. For a CPU stress test, make sure “Stress CPU” is checked. You can also choose to stress other components, but for this guide, we focus on the CPU.
- Start the Test: Click “Start.” AIDA64 will now apply a heavy load to your CPU.
- Monitor Temperatures: Watch your CPU temperatures closely. Use your temperature monitoring tool.
- Observe for Errors: Watch for any errors or instability. This includes system crashes, blue screens, or freezes.
- Stop the Test: After a sufficient time (usually 15-30 minutes for initial testing, longer for stability confirmation after overclocking), click “Stop.”
Interpreting the Results
- High Temperatures: If your CPU temperatures reach very high levels (above 90-95°C for most CPUs), your cooling solution might not be adequate.
- System Instability: If your system crashes or freezes, your CPU is not stable under the applied load. This could be due to overheating, incorrect BIOS settings, or a faulty CPU.
Safe Temperatures
- Idle: 30-45°C
- Load (Stress Test): Under 85°C is generally considered safe for prolonged use. Temperatures above 90-95°C can be dangerous and may damage your CPU over time.
Troubleshooting Instability
If you experience instability during the stress test:
- Check Cooling: Make sure your CPU cooler is properly installed and functioning.
- Check BIOS Settings: If you have overclocked your CPU, review your BIOS settings. You may need to reduce the clock speed or increase the voltage (with caution).
- Update Drivers: Ensure your motherboard chipset drivers are up to date.
How Long to Stress Test
- Initial Test: 15-30 minutes. This is enough to identify major issues.
- Stability Confirmation: 1-2 hours or even longer (up to 24 hours in some cases). This is for confirming long-term stability, especially after overclocking.
Stress testing your CPU with AIDA64 is a valuable way to ensure system stability and identify potential problems. By following these steps and monitoring your CPU temperatures, you can keep your computer running smoothly and avoid costly hardware damage. Remember to prioritize safe temperatures and address any instability issues promptly.
Key Takeaways
- AIDA64 stress tests reveal CPU stability and performance under heavy loads
- Users can customize tests to focus on specific system components
- Real-time monitoring helps identify potential issues during the stress test
Preparing for a CPU Stress Test
CPU cooling is very important for system performance and longevity. A good CPU cooler keeps the CPU at safe temperatures. This prevents thermal throttling. Thermal throttling is when the CPU reduces its clock speed to prevent overheating. This can significantly reduce performance. There are different types of CPU coolers.
These types include air coolers and liquid coolers. Air coolers use heat sinks and fans. Liquid coolers use a water block, radiator, and pump. Liquid coolers are more effective at cooling high-performance CPUs. Choosing the right CPU cooler depends on your CPU, your budget, and your needs.
Before running a CPU stress test with AIDA64, proper preparation is crucial. This involves understanding the software, meeting system requirements, and configuring the right parameters.
Understanding AIDA64
AIDA64 is a powerful system diagnostic tool that offers comprehensive CPU stress testing capabilities. It can evaluate multiple threads, cache, and memory performance.
The software provides detailed hardware information and benchmarking features. Users can monitor temperatures, voltages, and fan speeds during tests.
AIDA64 offers both free and paid versions. The paid version, AIDA64 Extreme, includes more advanced testing options.
System Requirements and Setup
To run AIDA64 effectively, users need a compatible operating system. Windows 7 or later is recommended.
A stable internet connection is necessary for downloading and updating the software. Users should close all non-essential programs before starting the test.
It’s important to ensure proper cooling for the CPU. Adequate airflow and functioning fans are essential.
Users should consider running additional monitoring tools like HWiNFO64 or Core Temp alongside AIDA64. These provide extra data points for temperature and performance.
Configuring AIDA64 Parameters
AIDA64 offers various stress test options. Users can choose to stress the CPU, FPU, cache, or memory.
The duration of the test is adjustable. Longer tests provide more thorough results but require more time.
Users can set temperature limits to prevent overheating. The software will stop the test if these limits are reached.
It’s advisable to start with default settings and gradually increase stress levels. This approach helps identify the CPU’s stable operating range.
AIDA64 allows users to log test results. Enabling this feature provides valuable data for analysis after the test.
Executing and Monitoring the Stress Test
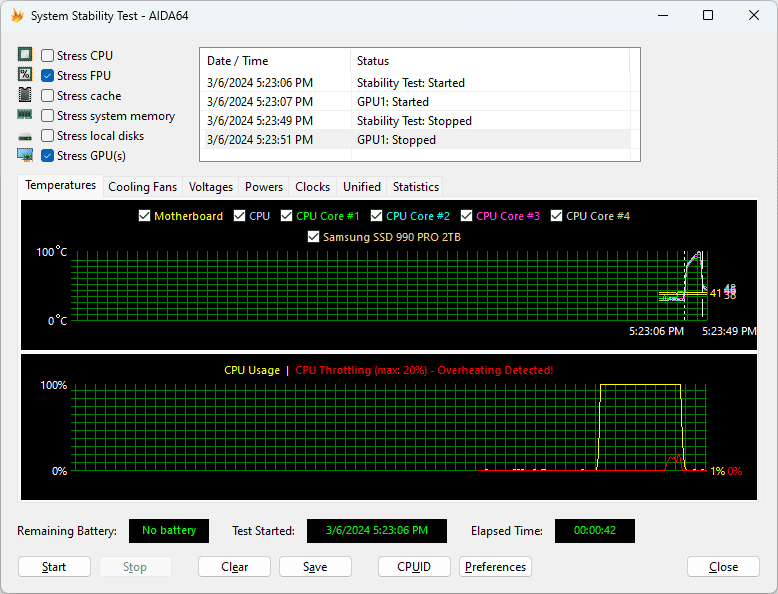
AIDA64’s System Stability Test provides a comprehensive way to evaluate CPU performance under heavy load. This process involves running the test, analyzing sensor data, and checking system temperatures.
Running the System Stability Test
To start the System Stability Test in AIDA64, users should open the tool and navigate to the “Tools” menu. Select “System Stability Test” from the options. The interface displays various test modules, including CPU, FPU, cache, and memory.
Users can choose specific modules or run all tests simultaneously. For a thorough CPU stress test, select at least the CPU and FPU options. Click the “Start” button to begin the test.
AIDA64 will push the CPU to its limits, utilizing all available cores and threads. The duration of the test can vary, but running it for at least 30 minutes is recommended for reliable results.
Interpreting Sensor Readings and Results
During the stress test, AIDA64 provides real-time sensor readings. These include:
- CPU temperature
- Clock speeds
- Voltage
- Power consumption
- Fan speeds
Users should monitor these values closely. High temperatures or unstable clock speeds may indicate potential issues with the CPU or cooling system.
AIDA64 displays this data in both numerical and graphical formats. Graphs help visualize trends over time, making it easier to spot anomalies or sudden spikes in temperature or power usage.
Pay attention to any error messages or system crashes during the test. These can point to instability or hardware problems that require further investigation.
Assessing System Cooling and Temperatures
CPU temperature is a critical factor during stress testing. Most modern CPUs have a maximum safe operating temperature between 70°C and 100°C. Users should consult their CPU manufacturer’s specifications for exact limits.
If temperatures approach or exceed these limits, it may indicate inadequate cooling. Possible solutions include:
- Improving case airflow
- Upgrading CPU cooler
- Reapplying thermal paste
Monitor fan speeds to ensure they’re responding appropriately to increased temperatures. Some users may need to adjust fan curves in BIOS settings for optimal cooling performance.
Compare idle temperatures to stress test temperatures. A difference of 30-40°C is typical, but larger gaps might suggest cooling issues.







