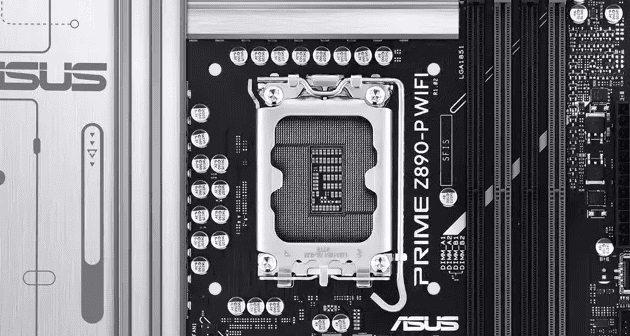
The LGA 1851 socket marks the latest advancement in Intel’s CPU connection technology. This new socket, designed for Intel’s upcoming Meteor Lake-PS and Arrow Lake-S desktop processors, features 1,851 pins – an increase of 151 pins from its predecessor, the LGA 1700. The additional pins aim to enhance support for PCIe 5.0 SSDs and improve I/O interfaces.
Intel released the LGA 1851 socket on October 24, 2024, introducing it as part of their new Intel Core Ultra x 2xx series. While the socket boasts more pins, it maintains the same dimensions and mounting hole distances as the LGA 1700. This design choice ensures compatibility with existing CPU coolers, making the transition easier for users upgrading their systems.
The LGA 1851 socket will be found on 800-series motherboards, offering improved performance and features for next-generation Intel processors. This upgrade positions Intel to compete more effectively with AMD’s AM5 socket, narrowing the gap in pin count and capabilities between the two platforms.
LGA 1851: Intel’s New Socket for Desktop CPUs
LGA 1851 is the latest CPU socket from Intel. It’s designed to support the company’s next-generation desktop processors, including Meteor Lake and Arrow Lake. This socket represents a significant upgrade from the previous LGA 1700 socket, bringing several key improvements and new features.
Key Features of LGA 1851
- More Pins: As the name suggests, LGA 1851 has 1851 pins, a notable increase from the 1700 pins in the previous generation. This allows for more power delivery and data transfer capabilities, crucial for the demanding performance of new CPUs.
- Support for New Technologies: LGA 1851 is designed to support the latest technologies integrated into Intel’s upcoming CPUs. This includes features like PCIe 5.0, DDR5 memory, and potentially even integrated AI accelerators.
- Improved Thermal Performance: The socket’s design incorporates improvements for better heat dissipation. This is essential for managing the thermal output of increasingly powerful processors.
- Backward Compatibility: While LGA 1851 is a new socket, it maintains some degree of backward compatibility with certain coolers designed for LGA 1700. This can make upgrading easier for some users.
Processors Compatible with LGA 1851

Currently, the following processor families are confirmed to be compatible with LGA 1851:
- Meteor Lake: Intel’s upcoming 14th generation of CPUs, featuring a new tiled architecture and significant performance improvements.
- Arrow Lake: Expected to succeed Meteor Lake, further refining the architecture and potentially offering even greater performance gains.
Motherboards with LGA 1851
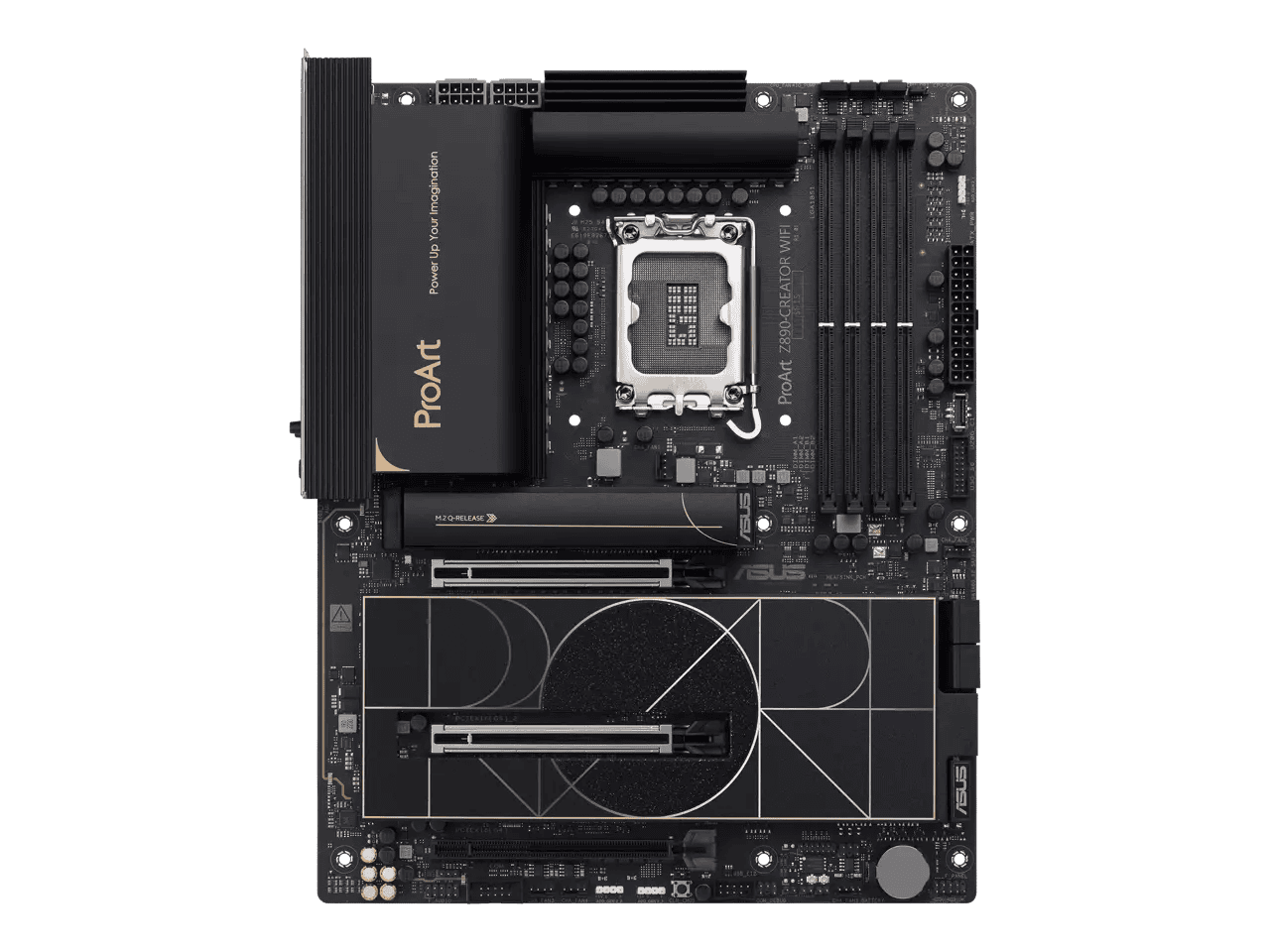
Several motherboard manufacturers, including ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, and ASRock, have already released motherboards with the LGA 1851 socket. These motherboards come with various chipsets, such as the Z890, and offer a range of features for different needs and budgets.
Should You Upgrade to LGA 1851?
If you’re planning a new PC build or looking to upgrade your existing system, considering a platform with LGA 1851 can be a good choice. It offers access to the latest CPU technologies and performance. However, if you have a relatively recent system with an LGA 1700 socket, upgrading might not be necessary immediately, especially if your current system meets your needs.
Understanding CPU Generations and Architectures
It’s important to understand that the LGA 1851 socket is tied to specific CPU generations and architectures. Here’s a simplified explanation:
- CPU Generations: Intel releases new generations of CPUs periodically (e.g., 12th gen, 13th gen, 14th gen). Each generation typically brings performance improvements and new features.
- Architectures: Underlying the CPU generations are different architectures (e.g., Alder Lake, Raptor Lake, Meteor Lake). These architectures represent significant changes in how the CPU is designed and how it processes information.
The LGA 1851 socket is specifically designed for the Meteor Lake and Arrow Lake architectures. These architectures differ from the previous Alder Lake and Raptor Lake architectures used in LGA 1700 CPUs. This is why a new socket is necessary.
Key Takeaways
- LGA 1851 adds 151 pins to improve support for PCIe 5.0 SSDs and I/O interfaces
- The new socket maintains physical compatibility with existing LGA 1700 CPU coolers
- Intel’s 800-series motherboards will feature the LGA 1851 socket for next-gen processors
Overview of LGA 1851 Socket
The LGA 1851 socket represents Intel’s latest advancement in CPU socket technology. It serves as the foundation for Intel’s new desktop processors, including the Intel Core Ultra x 2xx series.
LGA 1851 features 1,851 pins, a 9% increase from its predecessor, the LGA 1700. This additional pin count enhances I/O interfaces and performance capabilities.
Intel designed this socket specifically for Meteor Lake-PS and Arrow Lake-S desktop processors. The company released LGA 1851 on October 24, 2024.
Compatibility is a key feature of the LGA 1851 socket. It maintains the same dimensions and mounting hole distances as the LGA 1700. This design choice allows users to use LGA 1700 coolers with LGA 1851.
The socket’s layout differs significantly from previous versions. This change accommodates the increased pin count and supports new processor features.
LGA 1851 positions Intel to compete more effectively with AMD’s AM5 socket. The increased pin count narrows the gap between the two platforms.

Motherboard manufacturers are preparing new designs to support LGA 1851. These boards will enable users to take full advantage of Intel’s latest processors and technologies.
Technical Specifications and Compatibility
The LGA 1851 socket introduces significant upgrades in processor support, memory capabilities, and power delivery. These enhancements enable improved performance and future-proofing for desktop systems.
Processor and Chipset Compatibility
LGA 1851 supports Intel’s Arrow Lake-S and Meteor Lake-PS processors. This socket is not backwards compatible with older CPUs. It features 1851 pins, an increase of 151 pins compared to the LGA 1700 socket.
The new socket works with Intel’s 800-series chipsets, including the Z890. These chipsets offer enhanced features and connectivity options. Intel plans to support future CPU generations on this platform, potentially including Lunar Lake.
Manufacturers have designed the socket to maintain physical compatibility with LGA 1700 coolers. This allows users to reuse existing cooling solutions when upgrading.
Memory and Expansion Support
LGA 1851 motherboards exclusively support DDR5 memory. This provides faster data transfer rates and improved efficiency compared to DDR4.
The platform offers expanded PCIe support. It includes 20 PCIe 5.0 lanes, with 16 dedicated to graphics cards and 4 for NVMe SSDs. An additional 4 PCIe 4.0 lanes support a second M.2 slot.
This configuration allows for high-speed storage and graphics capabilities. It caters to users who require top-tier performance for gaming or content creation.
Power and Cooling Requirements
LGA 1851 CPUs are expected to have similar TDP ratings to their LGA 1700 predecessors. However, the increased pin count may allow for more efficient power delivery.
The socket maintains the same 45×37.5mm dimensions as LGA 1700. This ensures compatibility with existing cooling solutions, simplifying upgrades for users.
Motherboard manufacturers are likely to implement robust power delivery systems. These will support the high-performance CPUs that the LGA 1851 socket is designed to accommodate.







