3D V-Cache is a groundbreaking technology developed by AMD for their processors. 3D V-Cache stacks additional layers of L3 cache on top of a CPU, significantly increasing cache size without enlarging the processor’s physical dimensions. This innovative approach enhances CPU performance, particularly in gaming and other cache-sensitive applications.
The technology works by vertically stacking cache memory directly on the processor die. This vertical stacking allows AMD to increase the total cache size without expanding the CPU’s footprint. The result is a substantial boost in L3 cache capacity, which can greatly improve data access speeds and overall system performance.
Gamers and power users stand to benefit the most from 3D V-Cache technology. The increased cache size allows the CPU to store more data closer to the processing cores, reducing the need to access slower system RAM. This leads to faster data retrieval and improved performance in tasks that require quick access to large amounts of data.
AMD’s Revolutionary 3D V-Cache: A Deep Dive
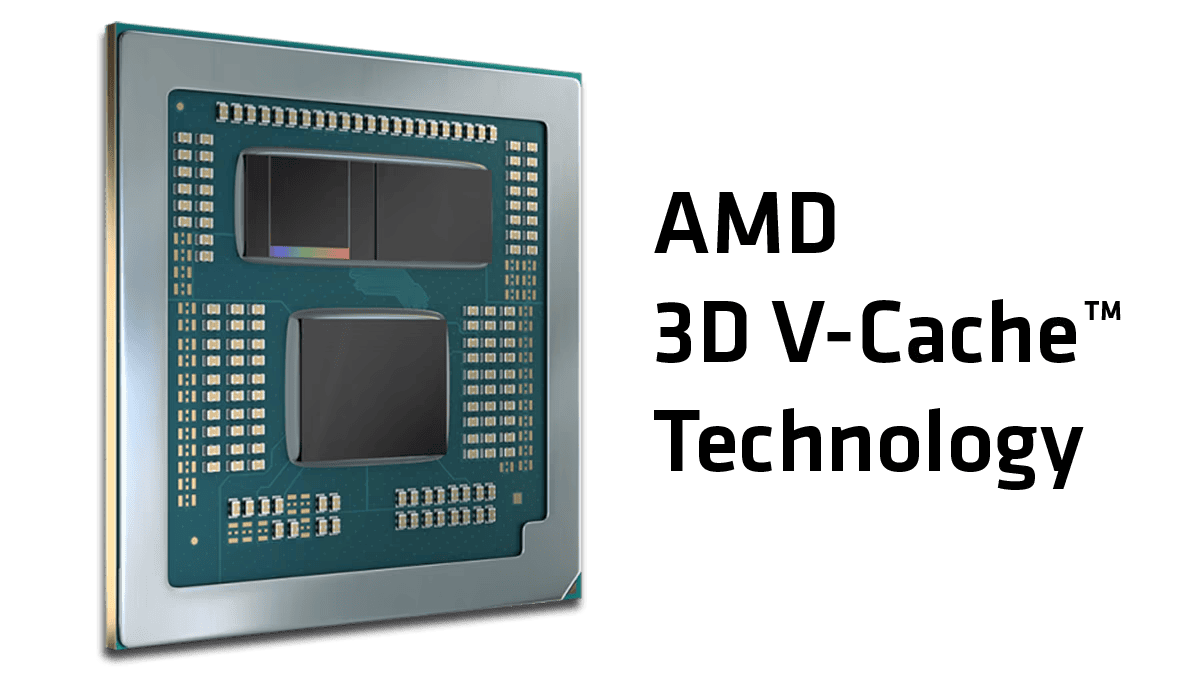
AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology is a game-changer in the world of processors. It’s a revolutionary approach to increasing CPU performance, particularly in gaming, by stacking additional cache memory directly on top of the processor die.
What is Cache Memory?
Before we delve into 3D V-Cache, let’s quickly recap what cache memory is. Your CPU uses cache as a high-speed memory buffer to store frequently accessed data and instructions. This allows the CPU to quickly retrieve information without having to access the slower main system memory (RAM). CPUs typically have multiple levels of cache:
- L1 cache: The smallest and fastest cache, located closest to the CPU cores.
- L2 cache: Larger and slightly slower than L1, but still much faster than RAM.
- L3 cache: The largest and slowest cache level, but it can hold more data.
How 3D V-Cache Works
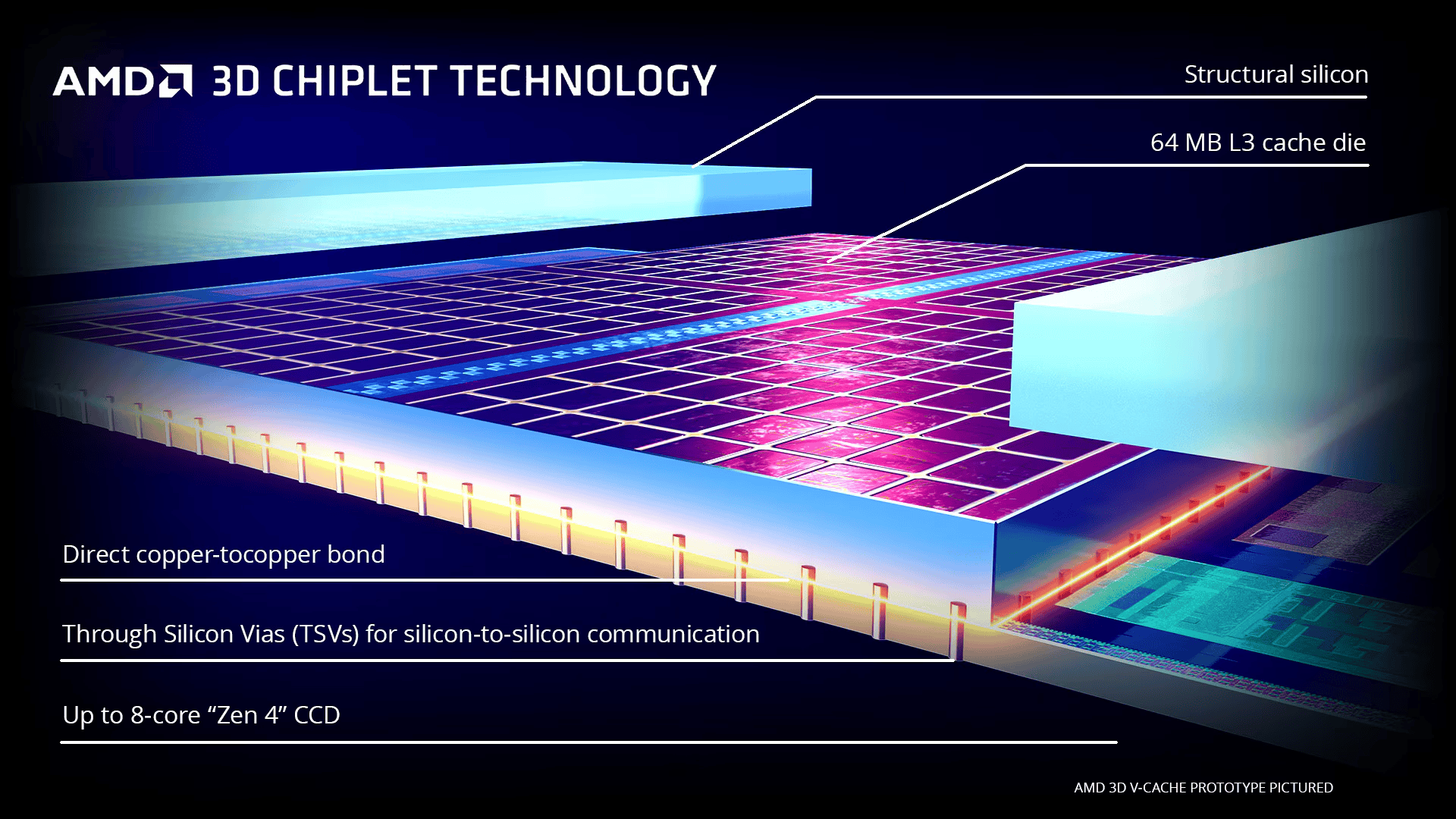
AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology focuses on dramatically increasing the amount of L3 cache available to the CPU. It does this by using a technique called “hybrid bonding” to vertically stack a dedicated L3 cache chiplet on top of the CPU die. This chiplet contains a massive amount of SRAM (Static RAM) cache, effectively multiplying the L3 cache capacity.
Benefits of 3D V-Cache
- Increased Gaming Performance: This is the most significant benefit. Games often need to access the same data repeatedly. With a larger L3 cache, the CPU can store more of this data, reducing the need to access slower system RAM. This results in:
- Higher frame rates: Smoother gameplay, especially at higher resolutions.
- Reduced latency: More responsive gaming experience.
- Improved 1% and 0.1% lows: Fewer stutters and more consistent performance.
- Improved Performance in Other Applications: While gaming is the primary focus, 3D V-Cache can also benefit other applications that rely heavily on cache, such as:
- 3D rendering and modeling: Faster processing of complex scenes.
- Scientific simulations: Improved performance in simulations that require large datasets.
The Evolution of 3D V-Cache
AMD introduced its first generation of 3D V-Cache with the Ryzen 7 5800X3D in 2022. This CPU featured a 64MB L3 cache chiplet, tripling the L3 cache compared to the standard Ryzen 7 5800X.
In 2024, AMD launched the second generation of 3D V-Cache with the Ryzen 7 9800X3D. This CPU boasts a 104MB L3 cache, further increasing performance and solidifying AMD’s leadership in gaming CPU technology.
The Future of 3D V-Cache
AMD has indicated that 3D V-Cache is a key technology for its future CPU roadmaps. We can expect to see even more powerful CPUs with larger cache sizes in the coming years. This technology has the potential to significantly impact not just gaming, but also other demanding applications that can benefit from increased cache capacity.
AMD’s 3D V-Cache is a groundbreaking innovation that has redefined CPU performance. By stacking cache vertically, AMD has unlocked a new level of gaming and application performance, setting a new standard for the industry.
Key Takeaways
- 3D V-Cache vertically stacks additional L3 cache on CPUs
- The technology significantly increases cache size without enlarging the processor
- Gamers and power users benefit from improved performance in data-intensive tasks
Understanding 3D V-Cache and Its Impact
AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology has revolutionized CPU performance. This innovative approach to cache design offers significant improvements in processing speed and efficiency.
3D V-Cache Technology Explained
3D V-Cache is a packaging technology that stacks additional layers of cache on top of a CPU. This vertical stacking allows for increased cache size without expanding the chip’s horizontal footprint. The technology uses through-silicon vias (TSVs) to connect the cache layers.
The primary benefit of 3D V-Cache is its ability to dramatically increase L3 cache size. For example, the Ryzen 7 5800X3D boasts 96MB of L3 cache, compared to 32MB in the standard 5800X. This larger cache reduces the need for the CPU to access slower system memory, improving overall performance.
AMD collaborates with TSMC to manufacture 3D V-Cache chips using advanced packaging techniques. This partnership enables the creation of high-performance processors with enhanced cache capabilities.
Differences Between Cache Levels
CPUs utilize multiple cache levels to optimize data access:
- L1 Cache: Smallest and fastest, located closest to the CPU cores
- L2 Cache: Larger than L1, but slightly slower
- L3 Cache: Largest and slowest of the three, shared among all cores
3D V-Cache specifically targets L3 cache expansion. While L1 and L2 caches remain crucial for immediate data access, the enlarged L3 cache acts as a more expansive buffer between the CPU and system memory.
This hierarchical structure allows the CPU to quickly access frequently used data, reducing latency and improving overall performance. The increased L3 cache size provided by 3D V-Cache technology further enhances this efficiency.
AMD Ryzen CPUs with 3D V-Cache
AMD has implemented 3D V-Cache in several Ryzen processors:
- Ryzen 7 5800X3D: The first consumer CPU with 3D V-Cache, based on Zen 3 architecture
- Ryzen 7000 X3D series: Including the Ryzen 9 7950X3D, featuring Zen 4 architecture
These CPUs offer significant performance gains, especially in gaming scenarios. The increased cache size allows for faster data access, reducing the need to fetch information from slower system memory.
Benchmarks have shown that 3D V-Cache CPUs can outperform their non-3D counterparts in various applications, particularly in games that benefit from larger cache sizes. However, the technology may result in slightly lower clock speeds compared to non-3D variants.
AMD continues to refine 3D V-Cache technology, with each new generation bringing improved performance and efficiency. This innovation has positioned AMD as a strong competitor in the high-performance CPU market.
Performance Aspects and Market Influence
AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology has significantly impacted CPU performance and market dynamics. This innovation enhances gaming and productivity while challenging competing processors.
Enhancements in Gaming and Productivity
3D V-Cache technology boosts gaming performance substantially. CPUs like the Ryzen 7 7800X3D excel in gaming benchmarks, often outperforming rivals. Frame rates see noticeable improvements, especially in CPU-intensive titles.
Productivity tasks also benefit from the increased cache size. Video editing and 3D rendering show performance gains. The larger cache reduces data access times, speeding up complex calculations.
AMD’s Ryzen 9 7950X3D showcases these advantages in both gaming and productivity. It combines high core counts with the benefits of 3D V-Cache.
Comparison to Competing CPUs
AMD’s 3D V-Cache CPUs compete strongly against Intel’s offerings. The Ryzen 7 7800X3D often outperforms the Core i9-13900K in gaming tests.
In productivity, the gap narrows. Intel’s higher clock speeds sometimes give it an edge in certain tasks. However, AMD’s larger cache benefits memory-intensive applications.
The performance-per-watt ratio favors AMD. 3D V-Cache CPUs typically have lower TDP ratings than comparable Intel chips.
Considerations for Overclocking and Thermal Management
Overclocking 3D V-Cache CPUs requires careful consideration. The added cache layers can impact heat dissipation.
AMD has implemented measures to manage thermals effectively. The 3D-stacked cache is placed strategically to optimize cooling.
Clock speeds on 3D V-Cache CPUs are often slightly lower than their non-3D counterparts. This helps maintain thermal balance. Despite lower clocks, the increased cache often results in better overall performance.
Users should ensure adequate cooling solutions when pushing these CPUs to their limits. Proper thermal management prevents throttling and maintains consistent performance.







