The possible manufacturing spin-off of Intel Foundry has become an important topic after CEO Pat Gelsinger unexpectedly retired. This change has caught the attention of industry analysts and competitors. Intel is now at a critical point as it deals with changes in leadership and competition. Discussions about a potential manufacturing spin-off highlight both opportunities and challenges in the semiconductor industry.

As interim leaders guide the company and a new CEO is chosen, their decisions in the coming months could determine Intel’s future in semiconductor innovation. It is crucial for Intel to stay committed to its manufacturing capabilities and explore strategic initiatives to regain its status as an industry leader.
Intel’s Manufacturing Strategy Under Scrutiny
The semiconductor industry is in a constant state of flux, with companies continually adapting to new technologies, shifting market demands, and evolving competitive landscapes. One of the most significant trends in recent years has been the rise of specialized chip foundries, which has prompted integrated device manufacturers to reevaluate their own production strategies.
Potential Spin-Off of Manufacturing Operations

Recent comments from Intel executives suggest the company might consider spinning off its manufacturing operations. This would create a separate entity focused solely on chip fabrication. This move could have profound implications for Intel and the wider semiconductor industry. Intel has been working to regain its manufacturing leadership.
The IDM 2.0 Strategy and its Challenges
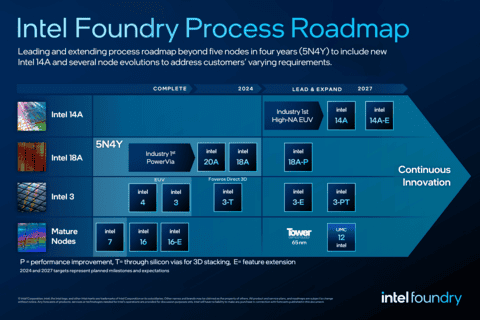
Intel’s current strategy, known as IDM 2.0 (Integrated Device Manufacturing), involves three key components:
- Maintaining internal manufacturing for its own chips.
- Using external foundries for some chip production.
- Offering foundry services to other companies.
While IDM 2.0 aims to provide flexibility and competitiveness, it faces challenges. The high cost of building and maintaining cutting-edge fabrication plants (fabs) puts a strain on resources. Separating manufacturing could free up capital for chip design and other areas.
Market Pressures and Competition
Intel faces intense competition from companies like TSMC and Samsung, which are leading pure-play foundries. These companies specialize in chip manufacturing and have invested heavily in advanced process technologies. This competition puts pressure on Intel to improve its manufacturing capabilities or consider alternative strategies.
Benefits and Drawbacks of a Spin-Off
A spin-off could provide several benefits:
- Increased Focus: Separate entities could specialize in their respective areas (design and manufacturing).
- Attracting Investment: A dedicated manufacturing company could attract investment specifically targeted at expanding fab capacity.
- Greater Flexibility: Intel could have more flexibility in choosing manufacturing partners, including its own spun-off entity.
However, there are also potential drawbacks:
- Loss of Integration: Losing direct control over manufacturing could impact the close integration between chip design and fabrication.
- Coordination Challenges: Managing relationships with a separate manufacturing entity could create logistical and coordination challenges.
Possible Outcomes and Industry Impact
A spin-off would reshape the semiconductor landscape. It could create a major new player in the foundry market, potentially altering the balance of power between existing foundries. This could also affect chip supply chains and pricing. It’s important to note that these discussions are still preliminary.
Potential Impacts of a Manufacturing Spin-Off
| Potential Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Specialization | Separate entities focus on design and manufacturing. |
| New Foundry Competitor | Spun-off manufacturing entity becomes a major foundry. |
| Changes in Supply Chain | Potential shifts in chip sourcing and manufacturing partnerships. |
| Financial Restructuring | Potential changes in investment and capital allocation. |
Short Summary:
- Pat Gelsinger’s sudden departure from Intel raises questions about the company’s future strategies, including a possible manufacturing spin-off.
- Intel is navigating a challenging landscape characterized by stiff competition, particularly in the AI chip sector, and aims to revitalize its operations.
- The interim leadership team is committed to sustaining Intel’s ambitious IDM 2.0 strategy while seeking a permanent CEO to steer the company forward.
In an unexpected turn of events, Intel has found itself at a crucial crossroads following the abrupt resignation of its CEO, Pat Gelsinger. His exit has led industry analysts to speculate on the potential spin-off of Intel Foundry, the company’s manufacturing arm. This development could redefine Intel’s position in the rapidly evolving semiconductor landscape, especially as industry dynamics shift toward artificial intelligence (AI) and contract manufacturing solutions.
Intel Under Leadership Transition
Gelsinger played a pivotal role during his tenure starting in February 2021, initiating substantial transformations within Intel, particularly within its Integrated Device Manufacturing (IDM) 2.0 strategy. This initiative emphasized enhancing manufacturing capabilities to regain market prominence. However, his departure raises significant questions about Intel’s direction, impacting not only the company itself but also the broader semiconductor market.
“Pat helped launch and revitalise process manufacturing by investing in state-of-the-art semiconductor manufacturing,” noted Frank Yeary, Intel’s Independent Chair of the Board. He acknowledged Gelsinger’s relentless drive for innovation and maintained that the company would continue to pursue its strategic priorities under the interim leadership of David Zinsner, Intel’s CFO, and Michelle Johnston Holthaus, the newly appointed CEO of Intel Products.
Market Dynamics and Competitive Pressures
The semiconductor industry is currently amidst a turbulent phase, heavily influenced by the explosive growth of AI technologies. Companies like Nvidia have leveraged this demand to capture significant market shares, prompting Intel to reevaluate its strategies to avoid lagging further behind. The company’s shares have plummeted by as much as 61% since the beginning of 2021, reflecting its struggles amidst fierce competition and missed opportunities in the AI chip segment.
As Intel grapples with an evolving market filled with challenges including the slowdown in consumer demand for PC processors and prolonged rollout timelines for new tech, the appointment of interim co-CEOs serves as a band-aid while the board embarks on a search for a permanent replacement. This leader will not only need to restore investor confidence but also align Intel’s operational focus with shifting technology trends, particularly in AI, data centers, and cloud computing.
Manufacturing Spin-Off Considerations
Industry experts predict that Intel may benefit from exploring a spin-off of its Foundry operations. Such a move could allow the semiconductor giant to streamline its operations and focus more on its core business while potentially attracting new investments. However, any definitive action will hinge on the direction provided by new leadership and Intel’s ability to stabilize its core business operations.
“The leadership transition presents an opportunity for Intel to reassess its operational structure and market focus,” stated Arjun Chauhan, an analyst at Everest Group. “A spin-off could unshackle the foundry from Intel’s overarching corporate structure, fostering new growth potential.”
Strategic Plans Amidst Financial Difficulties
Amid these leadership changes, Intel faces financial hurdles, including reports of a staggering 85% year-on-year profit downturn. Many analysts believe a drastic revamp is necessary for the company to reclaim its footing in the industry. In light of Gelsinger’s departure, quarterly losses and sweeping job cuts of approximately 15,000 demonstrate a stark reality that Intel must confront.
Intel’s current focus involves significantly trimming operational costs while still investing in key manufacturing initiatives. Gelsinger hinted at “decisive actions” to enhance the company’s financial health, laying the groundwork for a more sustainable future.
Intel’s Commitment to Foundry and Future Prospects
The commitment to Intel’s Foundry Services segment remains unwavering, as the company is actively enhancing this arm of its business, which has become integral in addressing the semiconductor shortage impacting industries worldwide. “We are focused on reducing operating expenses, capital expenditures, and cost of sales while maintaining core investments to execute our strategy,” Gelsinger stated in a firm directive to employees, underscoring the importance of the foundry element in Intel’s broader growth strategy.
Moreover, the prospect of an IPO for Altera, another Intel division, was reaffirmed—aiming for a public offering by 2026. This move could signal a strategic shift, allowing Intel to unbundle segments of its operations that fit well into the venture capital landscape while possibly freeing up liquidity for investment in AI and advanced process technologies essential to its future vision.
“Intel’s decision to spin off Altera signals a strategic shift aimed at unlocking liquidity, reinvesting into core growth areas, such as advanced process technology and AI,” Chauhan noted.
Future Leadership and Market Positioning
The interim co-CEOs Zinsner and Holthaus have reiterated their commitment to advancing Intel’s IDM 2.0 strategy, focused on production centralization and a fortified supply chain management approach. As they steer the company during this transitional phase, their leadership will be crucial to maintaining the integrity of Intel’s mission to reaffirm its reputation as a leading innovator in the semiconductor industry.
The search for a permanent CEO is expected to attract candidates with diverse backgrounds and innovative perspectives that align with the company’s ambitious goals. The newly appointed leader will face the challenge of preempting competitors and leveraging Intel’s resources to innovate in an environment increasingly marked by the urgency of AI and emerging technologies.
Broader Industry Implications
As Intel pivots amidst internal changes and external pressures, industry observers are attuned to how these shifts may reshape competitive dynamics among established players and emerging contenders. The potential spin-off of Intel’s manufacturing unit could set a precedent, encouraging other companies in the semiconductor sector to reconsider operational models while navigating the intricacies of financial performance and market demand.
“This transition is not just about Intel; it underscores a broader industry reconfiguration driven by technological evolutions and market necessities that competitors will have to adapt to,” Chauhan added.